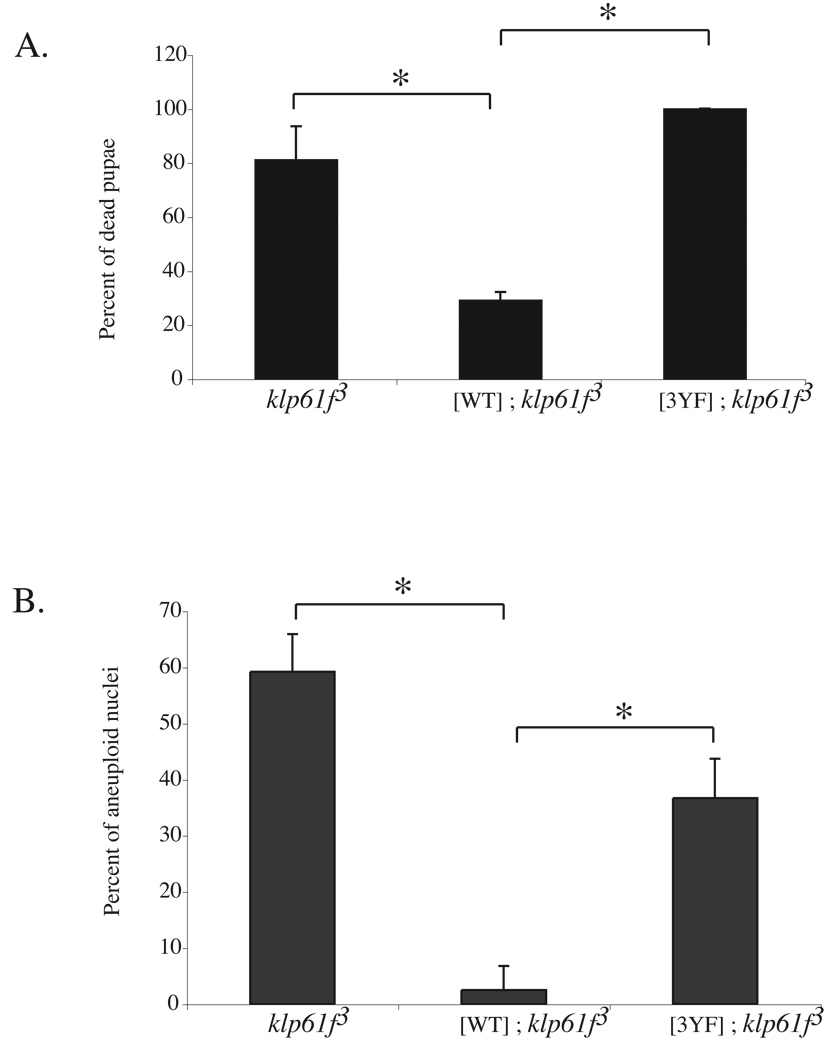
Figure 3. Phospho-accepting tyrosines in the head domain are important in vivo.
(A–B) Pupal lethality of klp61f3 mutants (A) and level of aneuploidy in klp61f3 mutant neuroblasts (B) are rescued by a Myc-KLP61FWT transgene ([WT]; klp61f3) but not a Myc-KLP61F3YF transgene ([3YF]; klp61f3). Data is represented as percentage of dead pupae (mean +/− SD from 3 embryo collections) in (A) and as percentage of aneuploid nuclei (mean +/− SD of nuclei from 3 larval brains) in (B). * indicates p < 0.01.