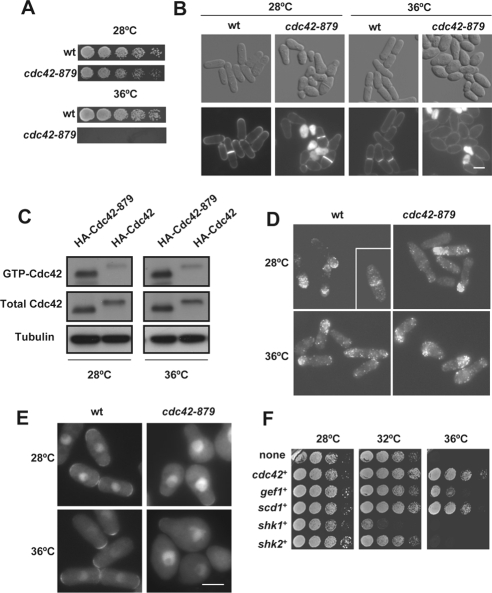
Figure 1.
Morphological defects of S. pombe cdc42-879 strain. (A) Growth of wild-type (wt) and cdc42-879 cells spotted at one-fourth dilution in YES medium and incubated at 28 or 36°C for 3 d. (B) Differential interference contrast (DIC) and fluorescence images of wt and cdc42-879 cells stained with calcofluor. Cells were grown at 28 or 36°C for 5 h. Bar, 5 μm. (C) Levels of GTP-bound Cdc42 in cdc42-879 cells. Extracts from wild-type and cdc42-879 cells grown at 28°C and transferred at 28 or 36°C for 3 h were precipitated with GST-CRIB and blotted with anti-HA antibodies (top). Total HA-Cdc42 in cell lysates was visualized by Western blot. Tubulin was used as loading control. (D) Immunofluorescence of HA-Cdc42 (wt) and HA-Cdc42–879 with anti-HA antibody. Both wild-type and mutant cdc42-879 cells were grown at 28°C and transferred at 36°C for 3 h. (E) Localization of GTP-bound Cdc42 by using wt and mutant cdc42-879 cells carrying integrated Gic2 CRIB-GFP. Cells were grown at 28°C and transferred at 36°C for 3 h. (F) Rescue of cdc42-879 thermosensitive growth defect by expression of Cdc42 pathway proteins. cdc42-879 cells were transformed with the expression plasmid pREP81X carrying either no insert, cdc42+, the coding genes for the GEFs gef1+ and scd1+, and the coding genes for the PAKs shk1+ and shk2+. Cells were grown on minimal media plates for 3 d at the indicated temperatures.