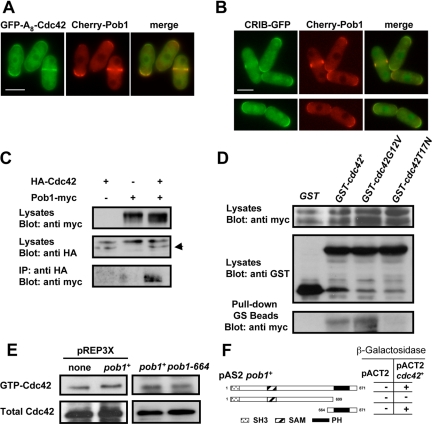
Figure 4.
Pob1 physically interacts with Cdc42 in a GTP-dependent manner. (A) Cells containing GFP-A8-Cdc42 and Cherry-Pob1 were grown to log phase and examined by fluorescence microscopy. (B) Cells containing CRIB-GFP and Cherry-Pob1 were grown to log phase and examined by fluorescence microscopy. (C) Extracts from cells expressing HA-Cdc42 and Pob1-Myc under their endogenous promoters were immunoprecipitated using anti-HA antibody and probed with anti-Myc antibody. Extracts were assayed for the level of HA-Cdc42 and Pob1-Myc by Western blot. Arrow points to HA-Cdc42 band. (D) Cells expressing endogenous Pob1-Myc were transformed with pREP1-GST, pREP1-GSTcdc42+, pREP1-GSTcdc42G12V, or pREP1-GSTcdc42T17N and grown in the absence of thiamine for 14 h. Cell extracts were pulled down with GS beads, and the precipitates were probed with anti-Myc antibody. Expression of Pob1-Myc and GST-Cdc42 alleles was analyzed by Western blot. (E) Pob1 does not regulate the amount of GTP-bound Cdc42. Extracts from wild-type cells, cells overexpressing pob1+, or pob1-664 cells carrying HA-cdc42+ incubated at 36°C for 5 h were precipitated with GST-CRIB and blotted with anti-HA antibodies (top). Total HA-Cdc42 in cell lysates was visualized by Western blot (bottom). (F) β-Galactosidase analysis of the two-hybrid interaction between Cdc42 and different fragments of Pob1. Several regions of the pob1+ ORF were cloned into pAS2 and used as bait for cdc42+ cloned into pACT2.