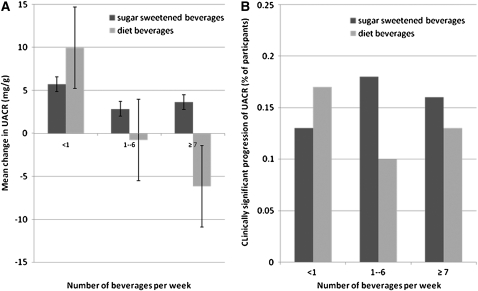
FIGURE 2.
Mean changes in the urinary albumin to creatinine ratio (UACR) (A) and the clinically significant progression of UACR (B) after sugar-sweetened and diet beverage intake per week. Significant progression was defined as a UACR <30 mg/g at examination 1 and ≥30 mg/g at examination 3 or a UACR >30 mg/g at examination 1 with an increase in UACR of ≥25%. The data reflect univariate relations; in multivariate analyses, point estimates for diet and regular soda were not significantly different. The patterns in panel A are highly influenced by comorbidities such as diabetic and hypertensive status. The bars in panel A reflect 95% CIs.