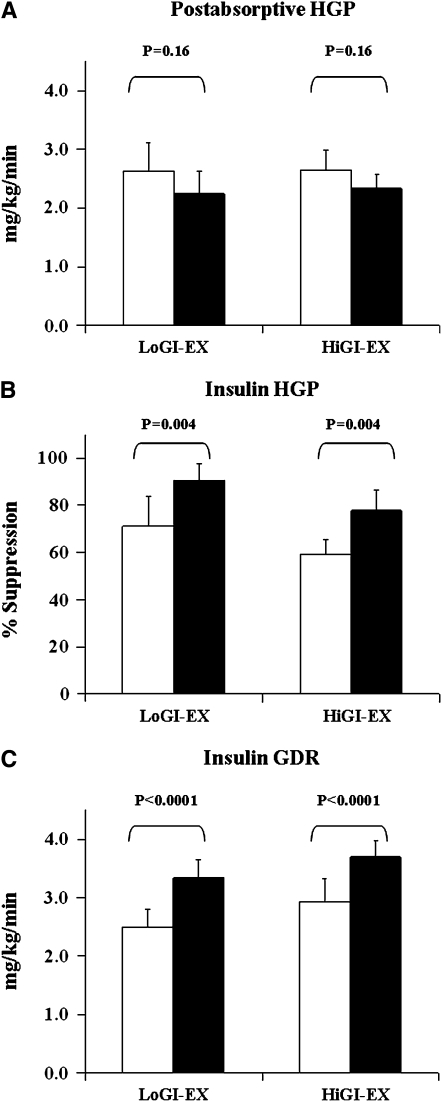
FIGURE 2.
Mean (±SEM) changes in glucose flux of 32 older, obese, and previously sedentary nondiabetic individuals who underwent a 7-d aerobic exercise training intervention (EX) combined with either a low–glycemic index (GI) diet (LoGI-EX; n = 15) or a high-GI diet (HiGI-EX; n = 17). White bars represent prestudy data; black bars represent poststudy data. A: Postabsorptive hepatic glucose production (HGP) showed a nonsignificant decline after the intervention (P = 0.16). B: The percentage of suppression of HGP by insulin increased after the study (P = 0.004). C: Insulin-stimulated glucose disposal rates (GDR) were significantly elevated after the intervention (P < 0.0001). These changes were not different between study groups, nor was there an effect of sex.