Figure 6. Reconstitution of Insulin RNA Cleavage by IRE1α in vitro.
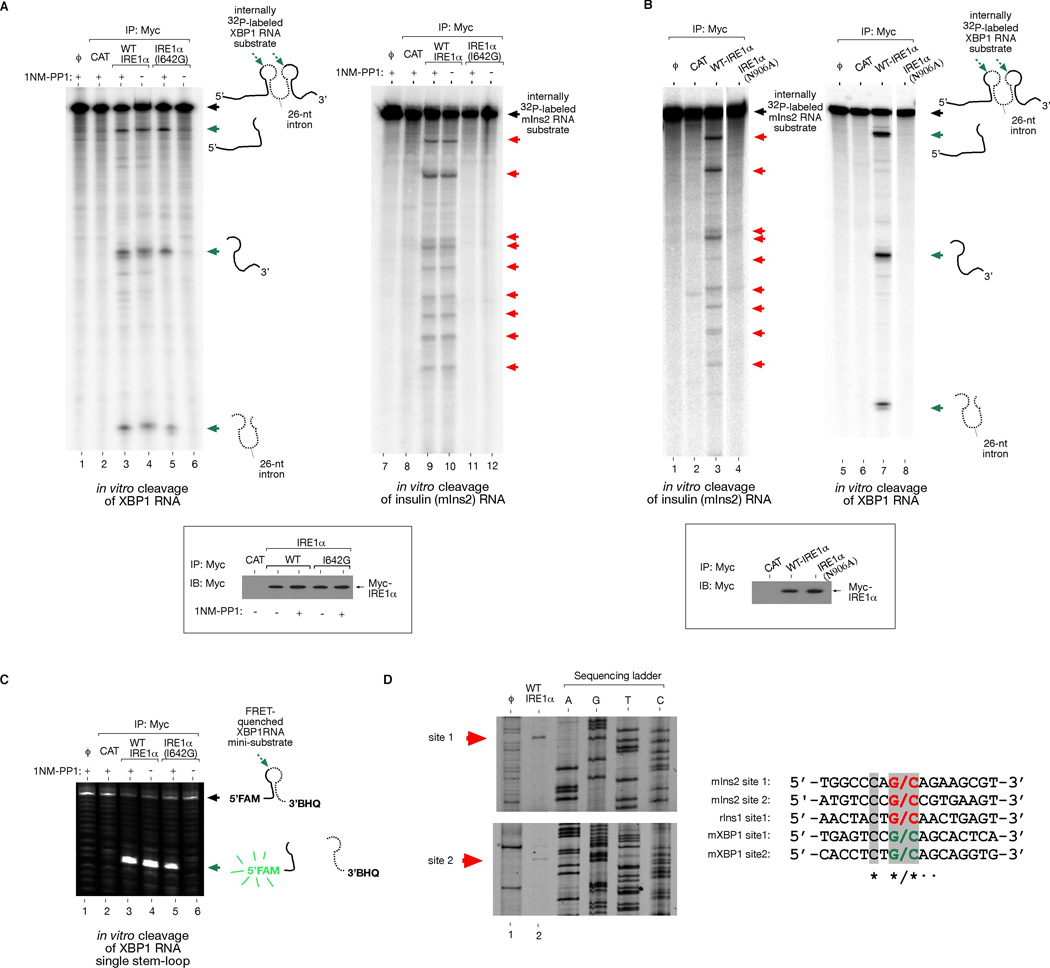
(A) In vitro cleavage of a 352 nucleotide (nt) XBP1 RNA encompassing the 26-nt intron, and a full-length 503-nt mouse Ins2 RNA by immunoprecipitated (i.p.) WT IRE1α and I642G proteins from T-REx 293 cells. ϕ=substrate alone; CAT=mock i.p. from T-REx 293 CAT cells. (B) Control reactions using kinase-active RNase-dead IRE1α (N906A) mutant. Anti-Myc immunoblot analysis show amounts of immunoprecipitated proteins used for in vitro cleavage reactions. (C) In vitro cleavage of 5’FAM -3’BHQ labeled XBP1 single stem-loop mini-substrate by WT IRE1α or I642G proteins +/− 1NM-PP1. ϕ=substrate alone; CAT= mock i.p. from T-REx 293 CAT cells. (D) Mapping of IRE1α cleavage sites in mouse Ins2 RNA, and sequence alignment with the cleavage sites of mouse XBP1 and rat Ins1 shows conservation. An asterisk * indicates complete nucleotide conservation, whereas ● indicates 4 out of 5 conserved nucleotides. See Figure S13 for cleavage site mapping of rat Ins1 RNA.
