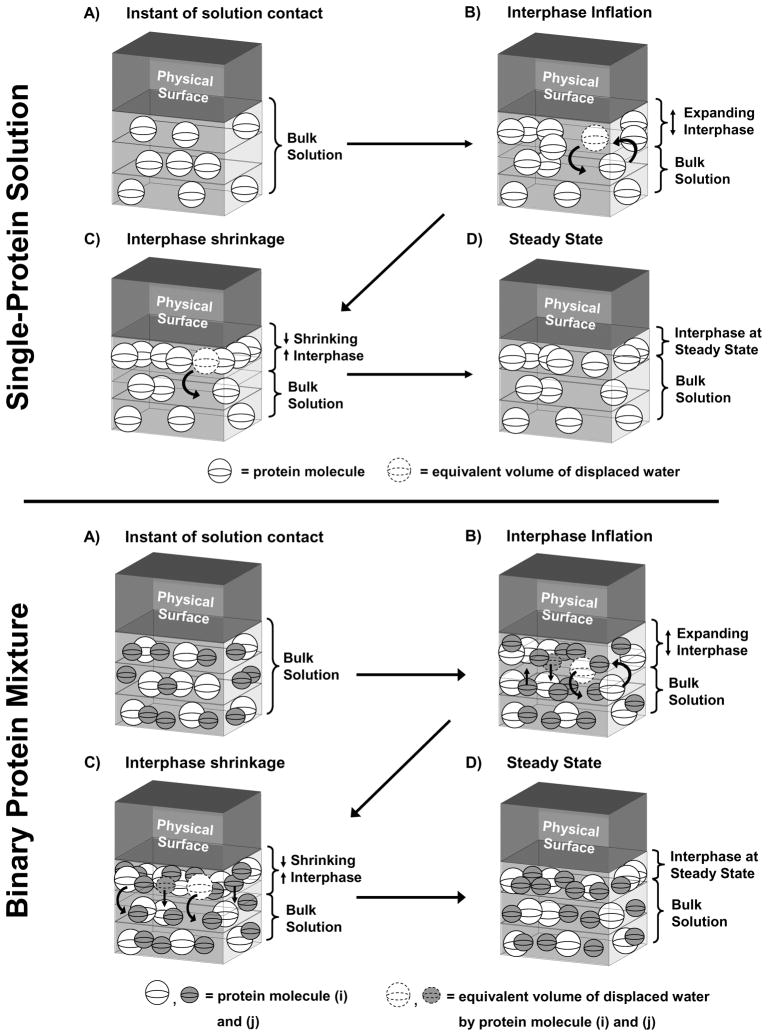
Figure 6.
Graphical illustration of the volumetric interpretation of single-protein adsorption (top panel group) and binary-adsorption competition between i, j proteins for the same hydrophobic adsorbent (bottom panel group). Essential steps depicted in both cases are: (Panel A) instantaneous creation of a thin interface between adsorbent (Physical Surface) and protein solution (Bulk Solution); (Panel B) rapid diffusion of proteins from solution into an inflating interphase region with concomitant displacement of interphase water; (Panel C) reorganization and concentration of protein within an interphase that is shrinking by expulsion of either interphase water (top panel group) or both interphase water and initially-adsorbed protein (bottom panel group); and (Panel D) attainment of steady-state interphase protein concentration by entrapment of initially-adsorbed protein in a minimal volume interphase (see Section 4.1 for detailed discussion).