Figure 1.
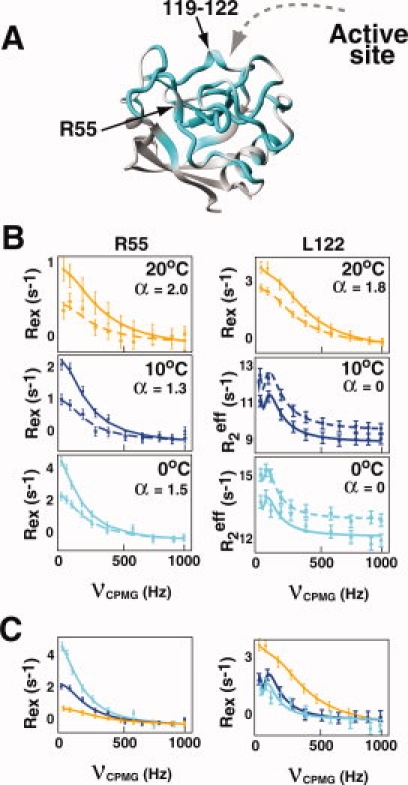
Free CypA undergoes exchange on multiple chemical shift timescales. (A) Nearly half of CypA exhibits chemical exchange contributions (cyan) above 0.5 s−1 (Supporting Information Table S1). (B) The static magnetic field dependence of chemical exchange is used to calculate α at 20°C, 10°C and 0°C from Supporting Information Table S2.23 R2-CPMG dispersion is shown at 600 MHz (dashed lines, ▪) and 900 MHz (straight lines, •) for R55 and L122. Dispersion curves for L122 at 10°C and 0°C exhibit no static field dependence (i.e. α = 0) and thus, the absolute R2eff is shown for clarity to avoid overlap of their calculated fits. (C) The temperature dependence of Rex is shown for these same residues and is in good agreement with the static magnetic field dependence. Rex increases with lower temperatures for R55 and decreases for L122, indicating fast exchange and slow exchange, respectively.1 Data were collected at 20°C (orange), 10°C (blue), and 0°C (cyan). [Color figure can be viewed in the online issue, which is available at www.interscience.wiley.com.]
