Figure 1.
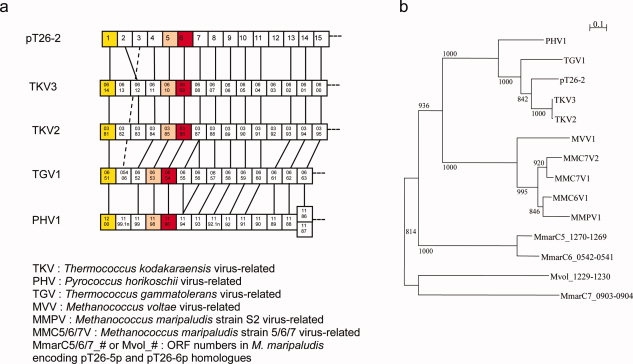
Genomic and phylogenetic repartition of pT26-5p and pT26-6p homologues. (a) Genomic organization of a part of virus-related integrated elements including pT26-6p homologues. Boxes represent putative ORFs, and numbers inside boxes correspond to the ORF numbers in the genomes. The yellow, pink and red boxes respectively represent the ORF encoding the C-terminal part of the integrases, the pT26-5 homologues and the pT26-6 homologues. Homologous ORFs are linked together (with doted line for a jumping link). (b) Unrooted maximum likelihood tree of concatenation of pT26-5p and pT26-6p homologues. 14 sequences from Thermococcales and Methanococcales were aligned by MUSCLE7 and 401 homologous positions were selected for tree calculation by PHYML8 using a JTT model of amino acid substitution. A gamma correction with four discrete classes of sites was used. The alpha parameter and the proportion of invariable sites were estimated. The robutness of the tree was estimated by non-parametric bootstrap analysis (1000 replicates) using PHYML. Scale bar represents the number of substitutions per site.
