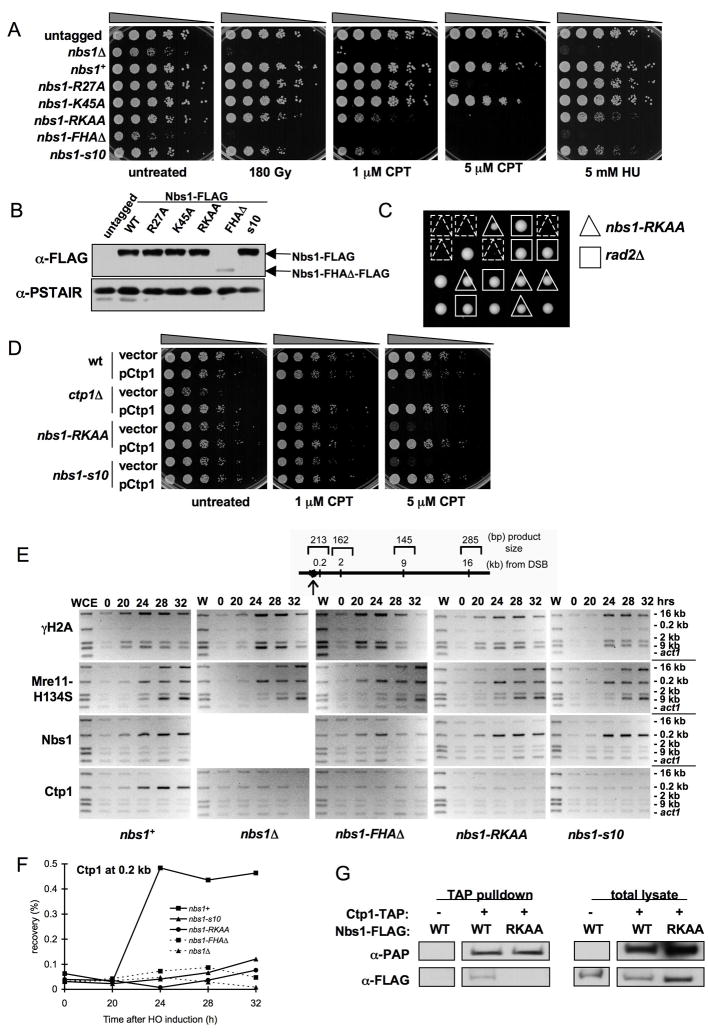
Figure 3. An Nbs1 FHA-defective Mutant Causes DNA Damage Sensitivity and Decreases Ctp1 Localization to DSBs.
(A) nbs1-RKAA (R27A/K45A) cells are sensitive to DNA damaging agents.
(B) Immunoblot of Nbs1-FLAG from strains used in (A). Expression of Nbs1-ΔFHA-FLAG is substantially decreased in soluble extracts relative to wild-type (wt). Immunoblot with PSTAIR antisera recognizing Cdc2 is used as a loading control.
(C) Tetrad analysis of a cross between rad2Δ and nbs1-RKAA strains. The rad2Δ/nbs1-RKAA double mutant is synthetic lethal, indicating a key role for the Nbs1 FHA domain in recombination-dependent DNA repair.
(D) Ctp1 is a multicopy suppressor of DNA damage sensitivity observed in the nbs1-RKAA mutant.
(E) ChIP analysis of γH2A, Mre11-H134S, Nbs1, and Ctp1 around a DSB created by HO endonuclease expressed from thiamine-repressible nmt1 promoter. Samples were collected at indicated times after depletion of thiamine from medium. Ctp1 localization at 0.2 kb from the DSB is defective in the nbs1 mutants.
(F) Quantitative real-time PCR was used to measure enrichment of Ctp1 at 0.2 kb from the HO endonuclease-induced DSB.
(G) Ctp1 associates with Nbs1 in an FHA domain-dependent manner. Strains were generated that express TAP-tagged Ctp1 and FLAG-tagged Nbs1 in an mre11-H134S background. IgG Sepharose beads were used to precipitate TAP-tagged Ctp1 and any associated proteins (negative control is a strain lacking Ctp1-TAP).