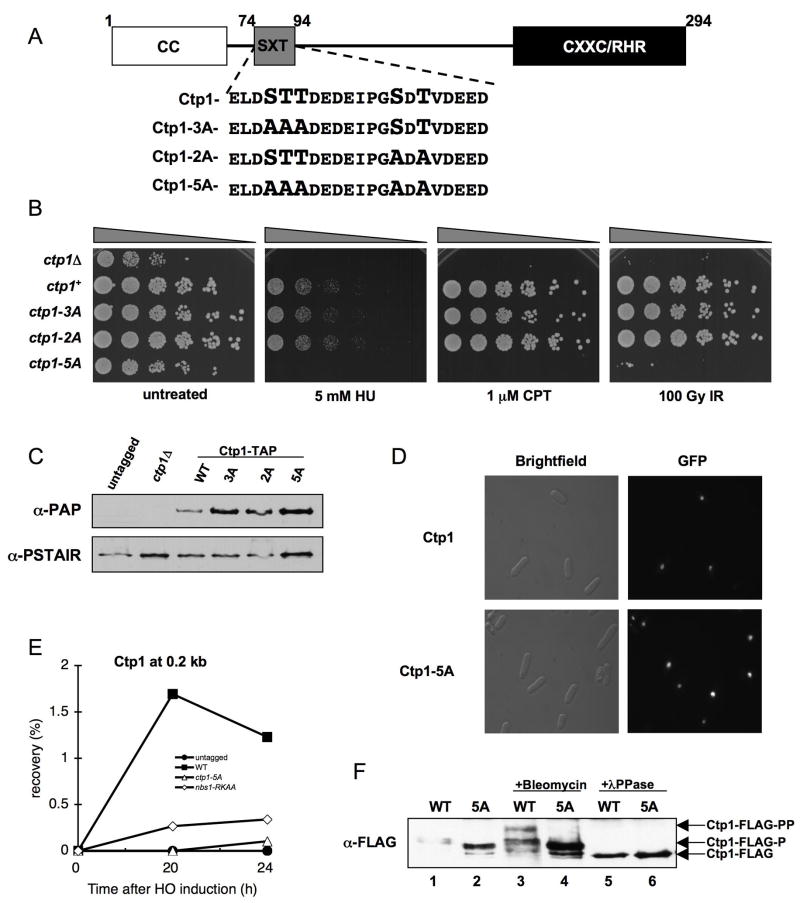
Figure 4. Phosphorylation Motif Required for Ctp1 Activity.
(A) Ctp1 schematic depicting conserved N-terminal coiled coil domain (CC), C-terminal core homology region (CXXC/RHR), and putative phosphorylation motif (SXT). Motif enlargement shows residue substitutions in the ctp1-3A, ctp1-2A, and ctp1-5A strains.
(B) ctp1-5A cells are sensitive to exogenous DNA damaging agents, similar to ctp1Δ cells.
(C) Ctp1-TAP immunoblot from strains used in (B), showing that Ctp1 mutants are expressed at levels at or above the wt amount (PSTAIR immunoblot loading control).
(D) GFP-Ctp1-5A intracellular localization is unaltered relative to GFP-Ctp1-wt.
(E) ChIP analysis of Ctp1 enrichment surrounding an HO endonuclease-induced DSB. Samples were collected at the indicated time after HO-induction. Ctp1 fails to localize to a site 0.2 kb from the DSB in the nbs1-RKAA and ctp1-5A strains.
(F) Basal phosphorylation is altered and damage-induced phosphorylation is abrogated in Ctp1-5A relative to wt. In asynchronous cells, Ctp1 is phosphorylated basally (Ctp1-FLAG-P), shown by increased Ctp1 mobility (Ctp1-FLAG) following λPPase treatment. After exposure to bleomycin, Ctp1 is hyper-phosphorylated, causing a decrease in mobility (Ctp1-FLAG-PP) relative to the basally phosphorylated form.