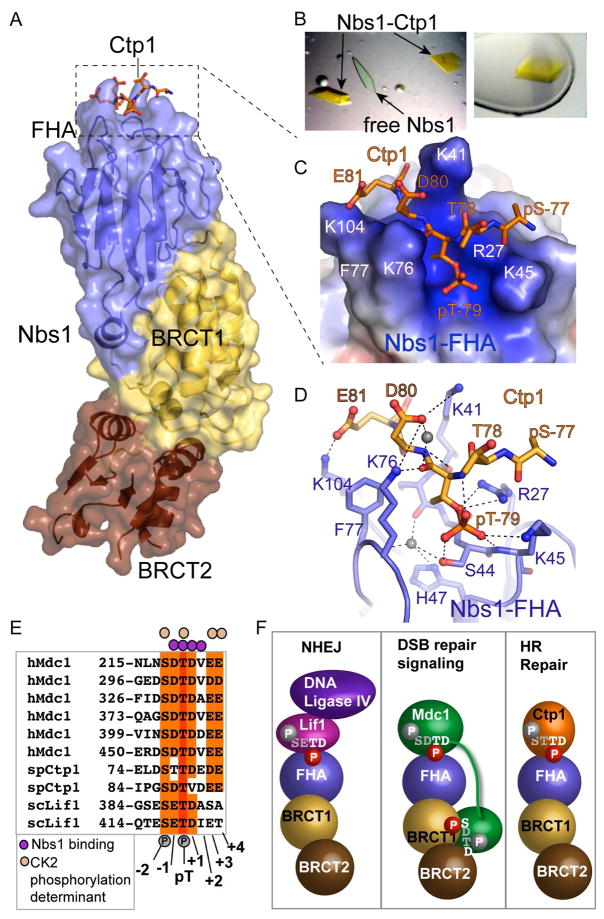
Figure 6. Nbs1-Ctp1 Complex.
(A) Overall structure. Ctp1 binds Nbs1 in a surface groove at the distal N-terminal FHA domain. Bound Ctp1 phosphopeptide (orange) is overlaid upon the Nbs1 surface.
(B) Left: Crystals of the Nbs1-Ctp1 complex (yellow) grow in a background of colorless free Nbs1-fc crystals. Right: Nbs1:Ctp1 co-crystal used for structure determination.
(C) Nbs1 FHA domain forms a positively charged groove (blue electrostatic potential) for binding Ctp1 acidic residues pThr79 and Asp80 (pThr(+1)) and Glu81 (pThr(+2)) in an extended conformation. Ctp1 (orange) is displayed overlaid upon an electrostatic surface representation of the Nbs1 peptide-binding surface.
(D) Nbs1-Ctp1 interaction details.
(E) Sequence alignment of Nbs1 interaction proteins shows key specificity.
(F) Schematic of known Nbs1 protein-phosphoprotein interactions regulating NHEJ, DSB signaling and HR repair. Residues with white and red phosphates are predicted to be key for Nbs1 interactions in the FHA or BRCT-BRCT phosphoprotein binding clefts, whereas grey residues and phosphates in the consensus are predicted to not make direct Nbs1 contacts.