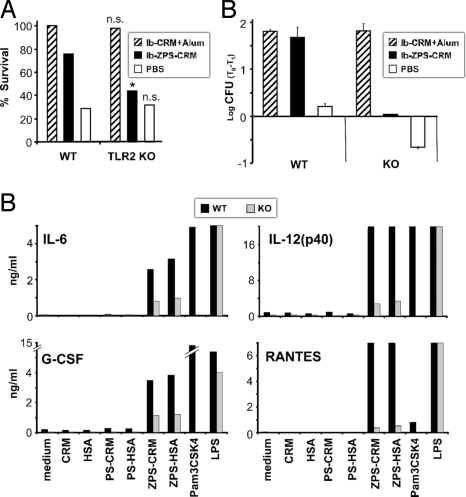
Fig. 4.
ZPS-conjugate activity in vivo is TLR2-dependent. (A) C57BL/6 wt and TLR2−/− mice on a C57BL/6 background were treated i.p. as indicated. WT and TLR2−/− female mice received three doses at day 1, 21, 35, and at day 38 all mice were coupled with wt males. The offspring from wt and TLR2−/− mice were injected s.c. with a lethal dose of GBS. The challenge doses were chosen to have the same percentage of survival for neonates born from wt or TLR2−/− mice treated with PBS. Significance was calculated by using Fisher's Exact Test. *, P < 0,05; n.s., not significant compared with the respective wt group. Data pooled from two independent experiments are shown. (B) Opsonophagocytosis assays were performed by using sera from wt and TLR2−/− mothers of (A). Triplicate results from sera diluted 1:100 were expressed as the mean log10 reduction in GBS colony-forming units before (T0) and after (T1) 60 min of incubation at 37 °C. (C) BM-DCs generated from the bone-morrow of wt or TLR2−/− mice were incubated for 20 h with ZPS and PS conjugates (10 μg/mL), CRM197 and HSA alone (10 μg/mL), and Pam3CSK4 or LPS (1 μg/mL). After 20 h of incubation the supernatants were assessed by Bio-plex analysis for cytokine and chemokine content. The production of IL-6, IL-12, G-CSF, and RANTES induced by ZPS-conjugates or Pam3CSK4 was considerably reduced in supernatants of BM-DCs generated from TLR2−/− mice. LPS induce the same cytokine and chemokine production in both genotypes. Data represent mean + SD of triplicates and are representative of two experiments.