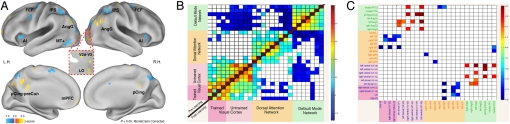
Fig. 3.
Whole-brain task-evoked modulation and spontaneous functional connectivity after perceptual learning. (A) Whole-brain voxel-wise z-map of trained minus untrained shape conditions, corrected for multiple comparisons (Monte-Carlo, P < 0.05) and projected onto an inflated representation of the PALS atlas. Central inset shows activation in the right dorsal visual cortex projected onto a flattened representation of the occipital lobe. Blue regions represent untrained > trained; orange regions represent response for trained > untrained. n = 12. (B) Pre- and postlearning spontaneous fcMRI. Color bar indicates z-transformed correlation values for each region pair, positive for red cells and negative for blue cells. Note stability of the correlation matrix across sessions (separated by >1 week), indicating that within-network functional connectivity is very stable over time (n = 14). (C) Post- minus prelearning changes in spontaneous fcMRI. Correlation matrix (Fisher z-transformed Pearson coefficient) of all possible ROI pairs in the visual cortex, dorsal attention network (DAN), and default mode network (DMN). Color bar indicates post- minus prelearning z-transformed correlation values (rest 2 – rest 1 scans) for each region pair. Blue cells represent significant correlation difference between dorsal attention and trained visual cortex ROIs (t test, P < 0.03, corrected for multiple comparisons): prelearning > postlearning. Red cells represent significant correlation difference between default network and untrained visual cortex ROIs, postlearning > prelearning; n = 14.