Figure 1.
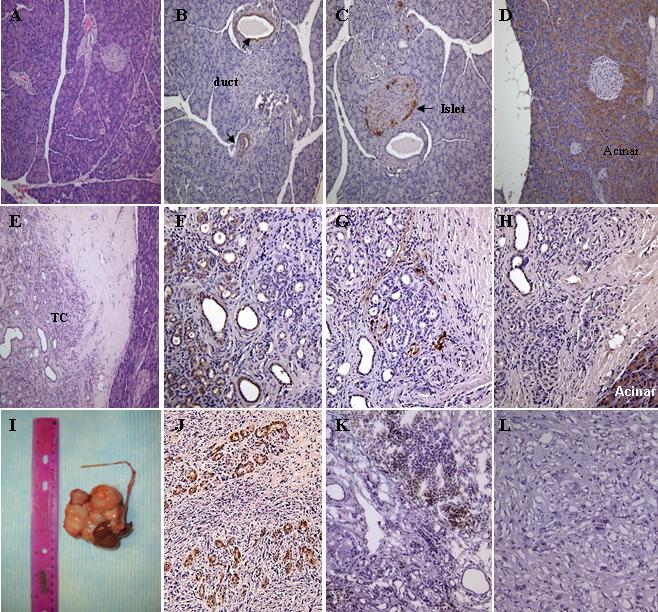
Characterization of MTC and tumor in the pancreas of animals received DMBA. (A) hematoxylin & eosin, (B) CK (arrows indicate pancreatic ducts), (C) chromogranin (arrow indicates pancreatic islet), (D) chymotrypsin staining of paraffin section of normal pancreas (Magnification 200x). (E) hematoxylin & eosin, (F) CK, (G) chromogranin, (H) chymotrypsin staining of paraffin section of pancreatic nodular lesion (Magnification 200x). (I) large tumor found near the DMBA implantation site. (J) CK staining of paraffin section of the tumor (Magnification 200x). (K) CD26 staining of frozen section of the pancreatic nodular lesion (Magnification 200x). (L) CD26 staining of frozen section of the tumor (Magnification 200x). All of the stainings except (A) and (E) were stained with immunoperoxidase conjugated antibodies. TC, tubular complexes.
