Figure 6.
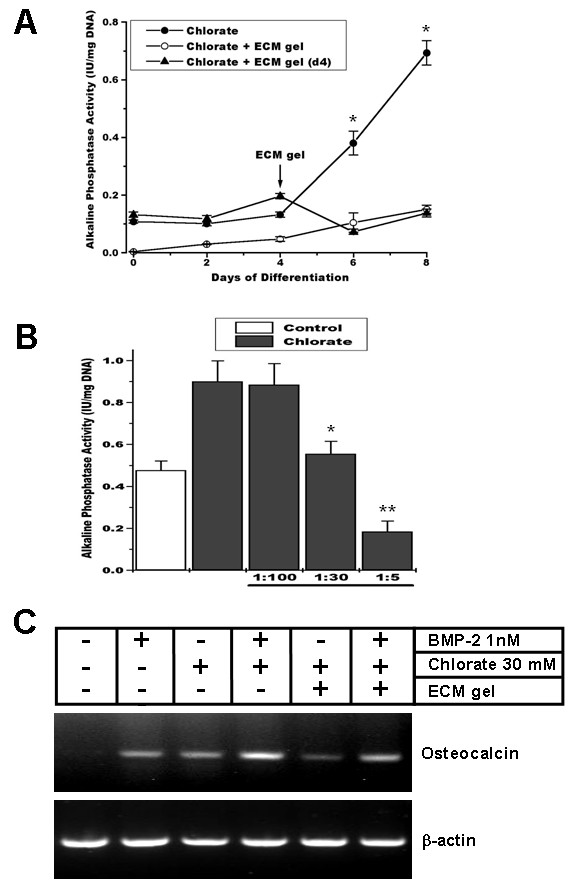
Addition of exogenous ECM prevents osteoblastic marker expression induced by inhibition of proteoglycan sulfation. A. C2C12 cells were induced to differentiate in the presence of 30 mM sodium chlorate (closed circles). ECM gel was added at day 0 (open circles) or at day 4 of differentiation (closed triangles). ALP activity was determined at different time points. Data are presented as mean ± S.E.M. of two independent experiments performed in triplicate (p < 0.0001, unpaired t-test between chlorate and ECM gel addition). B. ALP activity was determined in C2C12 cells induced to differentiate for 8 days in the absence (control) or presence of 30 mM sodium chlorate (chlorate) and different ECM gel dilutions were added to the cell culture. Data are presented as mean ± S.E.M. of two independent experiments performed in triplicate. * = significantly different from chlorate without and with 1:100 ECM gel, p < 0.05; ** = significantly different from all the other conditions p < 0.05 (ANOVA followed by Tukey-Kramer multiple comparisons test between chlorate conditions). C. RNA was extracted from C2C12 cells after 6 days of differentiation in the presence or absence of 30 mM sodium chlorate, 1 nM BMP-2, and/or ECM gel. After reverse transcription using Oligo-dTs the cDNA was amplified using specific primers for osteocalcin and β-actin.
