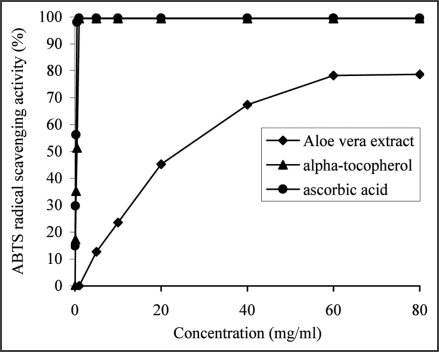
Figure 2.
The ability of the aqueous extract from Aloe vera leaf or α-tocopherol and ascorbic acid, used as reference antioxidants to scavenge ABTS*+ was estimated as a function of increasing extract (from 5 to 60 mg/ml) or α-tocopherol (from 0.125 to 1 mg/ml) and ascorbic acid (from 0.0625 to 0.5 mg/ml) concentrations and by recording the decrease in absorbance at 734 nm. The results were expressed as a mean percent scavenging activity of the extract (from 12.6 ± 0.96 to 78.2 ± 0.85%), α-tocopherol (from 17.2 ± 0.43 to 99.4 ± 0.45%) and ascorbic acid (from 14.8 ± 0.78 to 98.03 ± 0.64%), derived from three separate assays. The extract (at 60 mg/ml) was significantly less effective (p < 0.05) than α-tocopherol (at 1 mg/ml) and ascorbic acid (at 0.5 mg/ml).