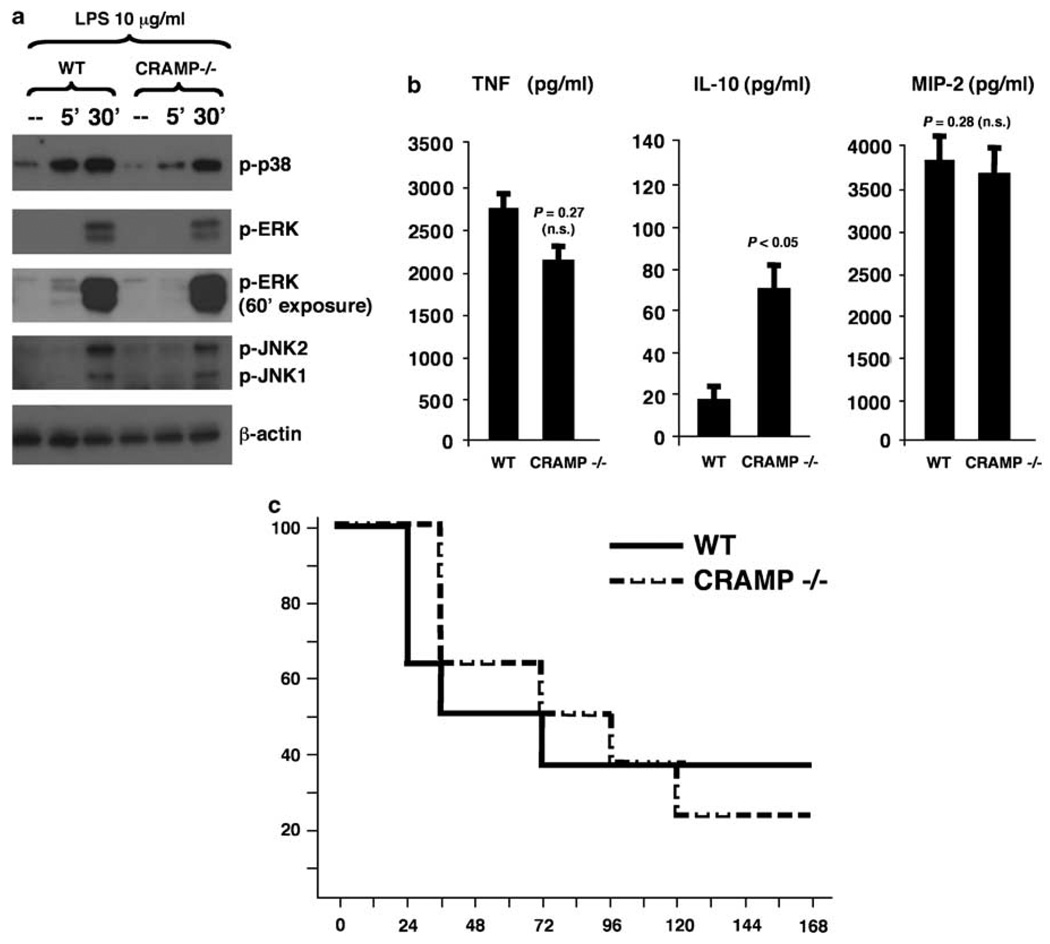
Figure 2.
Endogenous cathelicidin production by macrophages does not block lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced inflammatory responses and CRAMP−/− mice are not hypersusceptible to to LPS-induced mortality. (a) Wild-type (WT) and CRAMP−/− bone-marrow-derived macrophages (BMDM) were stimulated with LPS and phosphorylation of mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPKs) was assessed by western immunoblot. (b) WT and CRAMP−/− BMDM were stimulated with LPS for 3 h and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNFα), interleukin (IL)-10 and macrophage inflammatory protein-2 (MIP-2) levels determined in the supernatant by enzyme-einked emmunosorbent assay (ELISA); experiments were carried out three times with similar results; representative result is shown. IL-10 could not be detected in non-stimulated cells. (c) WT and CRAMP−/− mice received intraperitoneal injection of LPS (250 µg per mouse), and mortality was recorded in the following 7 days (n=8 mice per group).