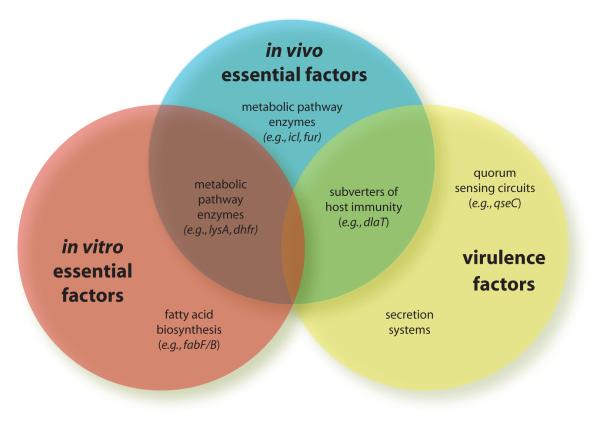
Figure 1. Virulence factors that represent potential targets for novel therapeutics in Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria.
1. toxin gene transcription, e.g. ToxT-dependent transcription of cholera toxin and toxin coregulated pilus in V. cholera 2. Quorum sensing, e.g. acyl-homoserine lactone (AHL) binding to transcriptional regulator LuxR in Gram-negative organisms 3. Secretion systems e.g. type III secretion in S. typhimurium 4. Adhesion e.g. pilus assembly in E. coli 5. Adhesion, e.g. carbohydrate binding motifs on pili in E. coli 6. Adhesion, e.g. sortase activity in S. aureus 7. Subverters of host immunity, e.g. CrtM production of staphyloxanthin in S. aureus