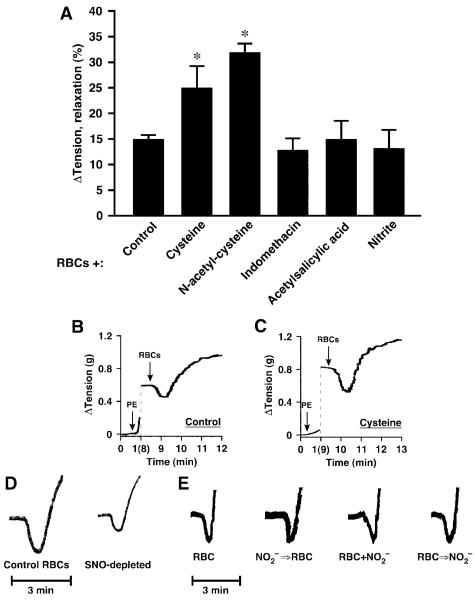
Figure 4.
Hypoxic vasodilation by native human RBCs of rabbit aortic segments. A, RBC-induced vasorelaxation was potentiated by cysteine and by N-acetylcysteine but was unaffected by nitrite or the prostaglandin synthesis inhibitors indomethacin and aspirin (all agents added 2 minutes before RBCs) (n=5 to 11). *P<0.05. B through D, Representative tracings illustrate the augmentation of relaxation by cysteine and the attenuation of relaxation by SNO-Hb depletion (≈80% depletion). E, Addition of nitrite to the bath (even at supraphysiological concentrations of 1 μmol/L, which are higher than those used in Cosby24) before (NO2-⇒RBC) or simultaneously with the addition of RBCs (NO2-+RBC), or near the termination of RBC-induced vasorelaxation (RBC⇒NO2-) had no discernible effect on the magnitude or duration of RBC-induced hypoxic vasodilation.