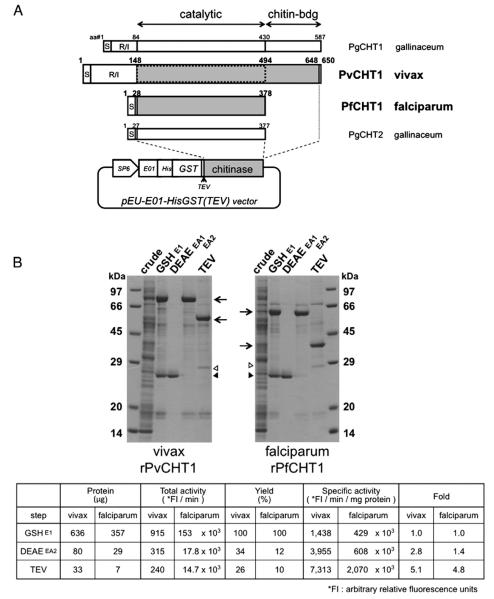
Fig. 1.
Synthesis and purification of recombinant P. vivax chitinase (PvCHT1) and P. falciparum PfCHT1 proteins. A. Schematic representation and translated sequence of PvCHT1 and PfCHT1 constructs in a cell-free expression vector pEU-E01-HisGST(TEV). The diagram of two P. gallinaceum chitinases PgCHT1 and PgCHT2 as well as the positions of signal peptide (S), repeat/insert region (R/I), and catalytic or chitin-binding domains are placed for comparison. The shaded regions are cloned to obtain recombinant (r) proteins. The second rPvCHT1 mimicking such a short form species as PfCHT1 is bordered by dotted line (see Section 2.1). The locations of SP6 promoter (SP6), translational enhancer (E01), hexahistidine (His), glutathione S-transferase (GST), and rPvCHT1 or rPfCHT1 (chitinase) on the vector are shown. B. A representative result after sequential purification steps (see Sections 2.3 and 2.4). 2.4 μl of total cell-free synthesis products (crude) or 10 μl of the samples at various purification steps were analyzed by SDS-PAGE under reducing condition. The protein products at each step are shown by arrows. 1) A contaminant glutathione (GSH)-binding protein in the eluates E1 after GSH/GST affinity chromatography, or in EA1 after DEAE anion exchange chromatography, and 2) the remnants of the N-terminal His-GST portion and possibly AcTEV protease itself (28–29 kDa) after AcTEV treatment and dialysis, are respectively shown by closed and open triangles. The chitinase specific activities of rPvCHT1 and rPfCHT1 samples are shown in the table format below; in the eluates E1, EA2, and in the final products after AcTEV treatment and dialysis.