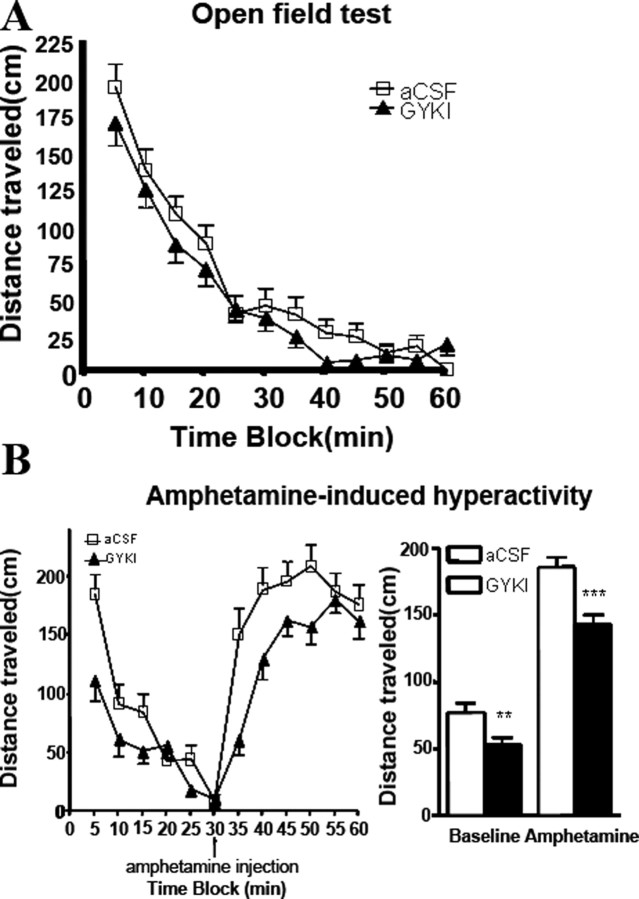
Figure 5.
Hippocampal infusion of AMPA receptor antagonist GYKI 52466 affects manic-like behaviors. Rats were implanted bilaterally with cannula systems for continuous delivery of either GYKI 52466 (50 μm) or vehicle (aCSF) control to the hippocampus. A, Open-field test. Eight days after surgery, rats were run in activity boxes for 60 min sessions. Distances traveled were scored by an automated tracking system. No significant differences were detected between treatment groups and controls for the 60 min time blocks or any of the constituent 5 min time blocks (n = 6; p > 0.05, unpaired t test). B, Amphetamine-induced hyperactivity. Ten days after surgery, rats were run in activity boxes for 30 min immediately followed by an intraperitoneal injection of 1 mg/kg amphetamine and placed back in the activity boxes for another 30 min. Distances traveled were scored as in the open-field test. Significant differences in baseline and amphetamine-challenged distances traveled between the control and GYKI 52466 groups were detected (n = 6; baseline: t = 2.806, **p = 0.0053; amphetamine: t = 4.272, ***p = 0.0001; unpaired t test). Error bars indicate SE.