Fig. 1.
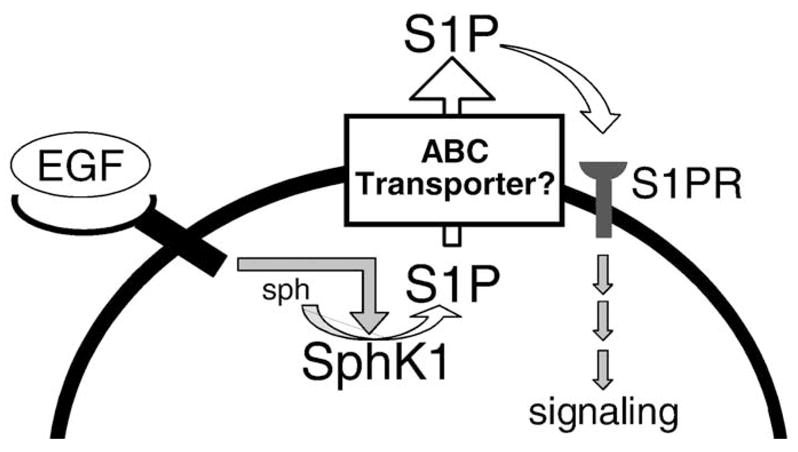
Formation, secretion, and actions of S1P. Many growth factors, including EGF, bind to a tyrosine kinase receptor, to stimulate and translocate SphK1 to the plasma membrane where its substrate sphingosine (sph) resides. This leads to spatially restricted formation of S1P that can be exported out of cells by ABC transporter family members. S1P can then bind to its receptors on the same or neighboring cells (S1PR) to stimulate G-protein regulated signaling pathways.
