Figure 8.
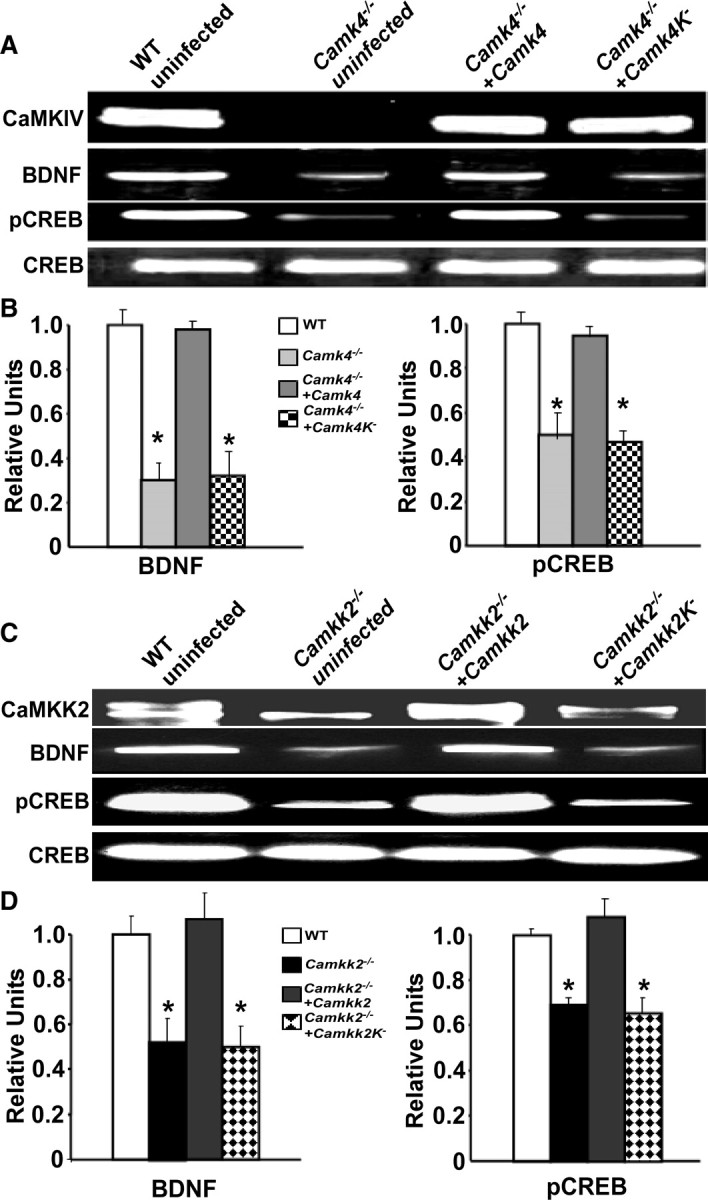
Lentiviral-mediated reexpression of CaMKIV or CaMKK2 restores pCREB and BDNF. A, Representative immunoblot of protein extracts derived from cultured WT and Camk4−/− GCPs or Camk4−/− GCPs which have been left uninfected, infected with either a lentiviral-CaMKIV-WT (active) or lentiviral-CaMKIV-K71M (inactive) construct. Note lower level of BDNF and pCREB in Camk4−/− GCPs. The reexpression of a catalytically active form of CaMKIV restored both BDNF and pCREB levels, whereas expression of the catalytically inactive CaMKIV-K71M did not restore BDNF or pCREB levels. B, Quantification of immunoblots after normalizing to total CREB (values shown are mean ± SEM; *p < 0.01 for difference against WT; n = 4 independent experiments). C, Representative Western blot analysis of protein extracts derived from cultured WT and Camkk2−/− GCPs or Camkk2−/− GCPs, which have been left uninfected or infected with either a lentiviral-CaMKK2-WT (active) or lentiviral-CaMKK2-K193E (inactive) construct. The lower molecular weight band seen so prominently in the Camkk2−/− lane is CaMKK1. Note that there is also reduced BDNF and pCREB protein in Camkk2−/− GCPs. The reexpression of a catalytically active form of CaMKK2 also restored both BDNF and pCREB levels, whereas expression of the catalytically inactive CaMKK2-K193E did not restore BDNF or pCREB levels. B, Quantification of immunoblots after normalizing to total CREB (values shown are the mean ± SEM; *p < 0.05 for difference against WT; n = 3 independent experiments).
