Fig 2.
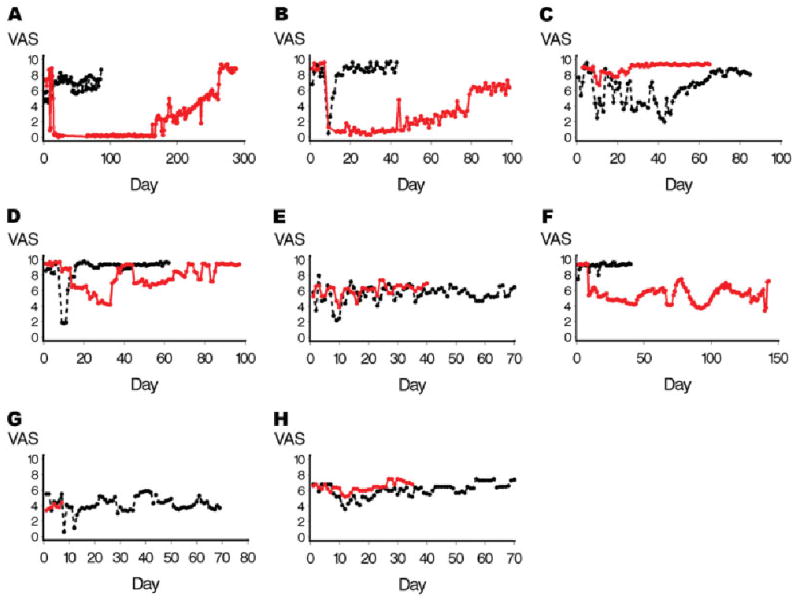
Change in visual analog pain score (VAS) over time. Botulinum toxin type A (BTA) reduces VAS sores of pain intensity over protracted time periods in responders. Assignment to the BTA-enhanced lumbar sympathetic block was associated with a mean decrease in VAS of 1.6 points (95% confidence interval, 1.2–2.0; p < 0.0001). Patients appear to be BTA responders or nonresponders. Despite refractory long-standing pain, Patients 1, 2, and 7 experienced long-term significant reduction in pain. Note time scales for each patient and each injection differ because each patient recorded pain until they perceived they had returned to baseline. All injections occurred on day 7 after a 1-week “run-in” period. Black lines represent bupivacaine; red lines represent bupivacaine plus BTA. Patients 1 (A), 2 (B), 4 (C), 5 (D), 6 (E), 7 (F), 8 (G), and 9 (H).
