Fig. 2.
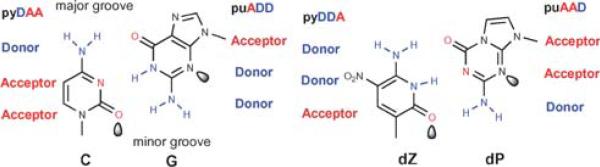
One example of an “artificially expanded genetic information system” (Aegis). Nucleobase pairs in this system have a Watson–Crick geometry, with large purines or purine analogs (indicated by “pu”) pairing with small pyrimidines or pyrimidine analogs (indicated by “py”) joined by hydrogen bonds. The hydrogen-bonding acceptor (A) and donor (D) groups are listed from the major to the minor groove as indicated. Lobes represent electron density in the minor groove. The nucleotides implementing the pyDDA:puAAD hydrogen bonding pattern (dZ:dP), the topic of this paper, are at the right.