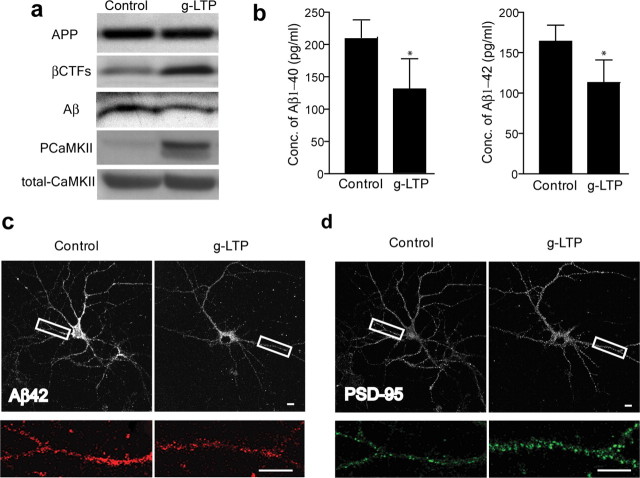
Figure 1.
Synaptic activation reduces intraneuronal Aβ and protects against reductions in PSD-95 at synapses of APP mutant neurons. a, Western blot of cell lysates demonstrates reduced levels of intraneuronal Aβ, increased levels of βCTFs, and unchanged levels of full-length APP in g-LTP compared with control treated Tg2576 neurons. The ratio of Aβ normalized to APP was decreased 38 ± 11% in g-LTP-treated compared with control-treated Tg2576 neurons (n = 8; p < 0.01). The ratio of βCTFs normalized to APP was increased 93 ± 41% in g-LTP-treated compared with control-treated Tg2576 neurons (n = 13; p < 0.05). b, Aβ1-40 and Aβ1-42 ELISA of neuron lysates from g-LTP and controls (n = 6; p < 0.05). c, g-LTP also reduced levels of intraneuronal Aβ42 by 39 ± 4% compared with control-treated Tg2576 neurons, as determined by confocal immunofluorescence (n = 5; p < 0.01). d, immunofluorescence shows that g-LTP increased levels of PSD-95 puncta 35 ± 10% compared with control-treated Tg2576 neurons (n = 5; p < 0.01). Scale bars, 10 μm.