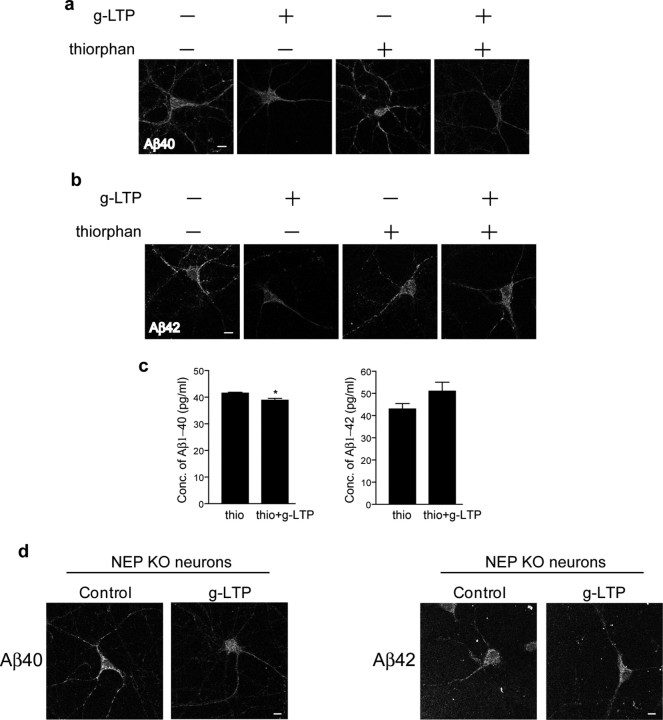
Figure 5.
Involvement of neprilysin in g-LTP induced reduction of intraneuronal Aβ42. a, Fluorescent immunolabeling of Aβ40 in g-LTP activated versus nonactivated Tg2576 neurons in the presence or absence of the neprilysin inhibitor thiorphan. Despite inhibition of neprilysin, g-LTP reduces intraneuronal Aβ40 by 12 ± 1% as demonstrated by confocal immunofluorescence (n = 3; p < 0.01). b, Fluorescent immunolabeling for Aβ42 in g-LTP activated versus nonactivated Tg2576 neurons in the presence or absence of the neprilysin inhibitor thiorphan. Inhibition of neprilysin prevents g-LTP induced reduction of intraneuronal Aβ42, as demonstrated by confocal immunofluorescence (n = 3). c, Aβ1-40 and Aβ1-42 concentrations measured by ELISA in neuron lysates from g-LTP and controls in the presence of thiorphan. Inhibition of neprilysin allows for synaptic activity-induced reduction of Aβ1-40 but not of Aβ1-42 (n = 3; p < 0.05 for Aβ1-40 values). d, g-LTP activated NEP KO neurons and NEP KO control neurons. g-LTP induces reduction of intraneuronal Aβ40 (left panels; 39 ± 12% reduction; n = 6; p < 0.01) but not Aβ42 (right panels; n = 6) in NEP KO neurons, as determined by confocal immunofluorescence. Scale bars, 10 μm.