Fig. 7.
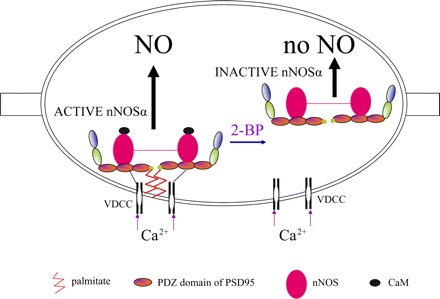
Cartoon summarizing the critical role of palmitoylation of PSD95 in catalytical activity of nNOS. The scaffolding protein PSD95 has 3 PDZ binding domains, a SH3, and a guanylate kinase domain. PDZ is an acronym for PSD95, Drosophila septate junction protein Discs-large, and the epithelial tight junction protein ZO-1. PSD95 is attached to the varicosity membrane by palmitoylation at the NH2-terminal end of PDZ1. nNOSα is attached to the PDZ2 domain of PSD95. PSD95 is also anchored to voltage-dependent calcium channels (VDCC) although the exact site of this interaction is not known. These interactions cluster nNOSα with VDCCs. Calcium influx causes CaM binding and activation of nNOS to produce NO. Treatment with depalmitoylating agent 2-BP results in dissociation of PSD95 and nNOSα from the varicosity membrane, leading to inactivation of nNOSα, causing loss of NO production.
