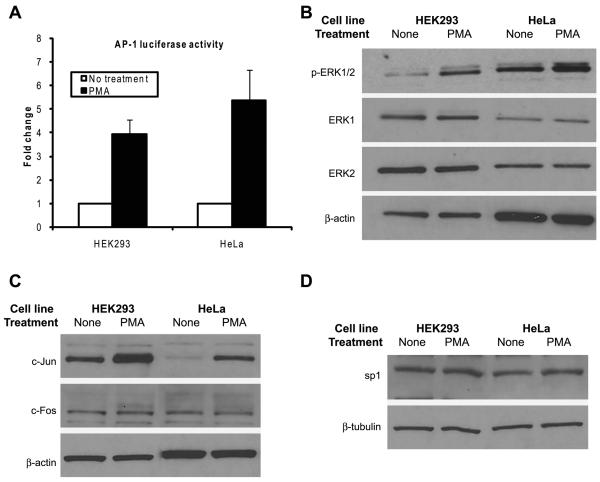
Fig. 6.
The activation of JNK and ERK is not solely sufficient for the induction of the HSV-1 TK promoter by PMA. A: HEK293 cells were transfected with 100 ng of AP-1 luciferase plasmid and, as an internal control, with 100 ng of SV40-β-galactosidase plasmid and HeLa cells were transfected with 100 ng of AP-1 luciferase plasmid and, as an internal control, with 20 ng of pRL-TK plasmid. At 24 hours post-transfection the cells were left non-treated or were treated with PMA for 8 hours. At the end of the treatment, the cells were harvested and firefly luciferase, Renilla luciferase and β-galactosidase assays were performed as appropriate. The firefly luciferase RLU values for HEK293 cells were normalized to those the β-galactosidase assay. The firefly luciferase RLU values for HeLa cells were normalized using the values for Renilla luciferase as a standard control. Fold change was calculated by setting the normalized RLU of the luciferase gene for the non-treated sample of the corresponding cell line to 1. The data shown are the mean and SD of three to five independent experiments. B: Overnight cultures of HEK293 and HeLa cells were either left non-treated or were treated with PMA for 15 minutes. At the end of the treatment the cells were harvested and immunoblotting for p-ERK1/2, ERK1 and ERK2 was carried out. C and D: Overnight cultures of HEK293 and HeLa cells were left non-treated or were treated with PMA for 8 hours. At the end of the treatment the cells were harvested and immunoblotting was performed for c-Jun, c-Fos and sp1.