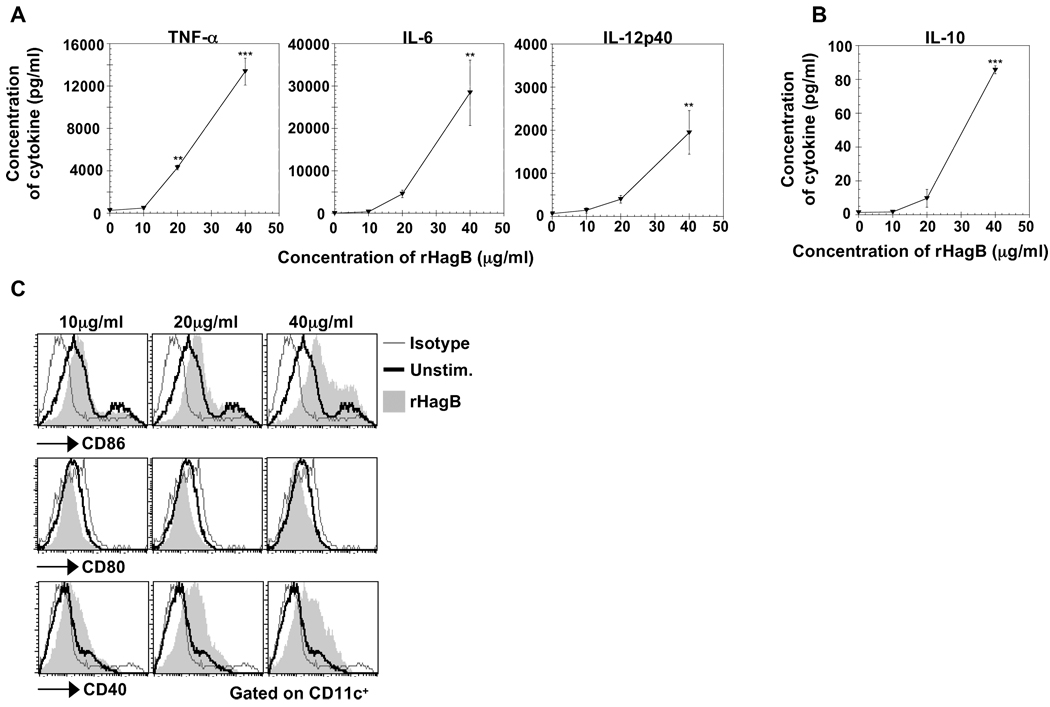
Fig. 1.
Stimulation of DC with rHagB results in the production of cytokines and the upregulation of costimulatory molecules. Bone marrow-derived DC (2×105) from WT mice were either unstimulated (0 µg/ml; negative control) or stimulated with 10, 20 or 40 µg/ml rHagB. Culture supernatants were harvested 24 h post-stimulation and assessed for the levels of the pro-inflammatory cytokines TNF-α, IL-6 and IL-12p40 (A) and the anti-inflammatory cytokine IL-10 (B) by ELISA. Results are expressed as the mean ± standard error of triplicate cultures from one of three independent experiments. ***, ** Significant differences at P < 0.001 and P < 0.01, respectively, compared to unstimulated cultures. (C) DC (2×105) from WT mice were stimulated with 10, 20 and 40 µg/ml rHagB for 16 h (shaded histograms) or left unstimulated as negative controls (thick lines). Cells were harvested and stained with fluorescent-labeled antibodies against CD11c, CD80, CD86, CD40 or matched isotype controls (thin lines). Histogram plots were gated on CD11c+ cells. Results represent one of three independent experiments.