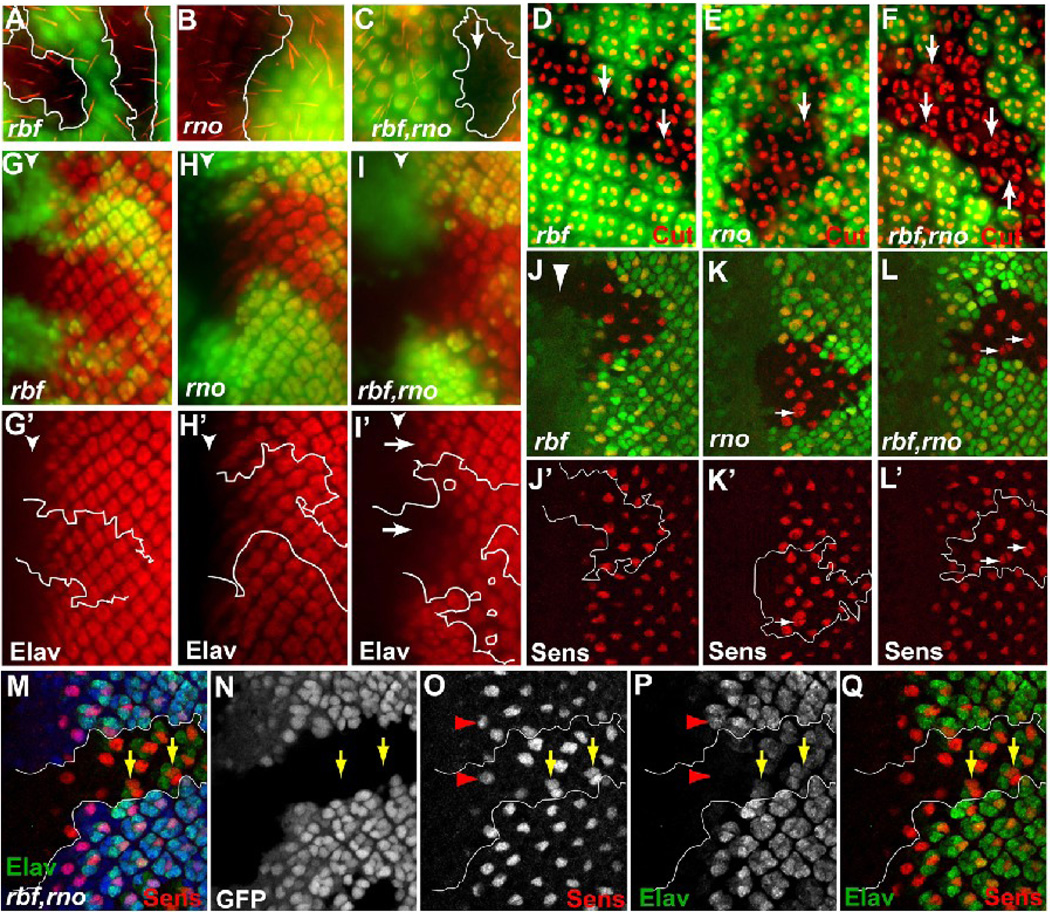
Figure 2.
Eye differentiation phenotypes of rbf,rno mutant clones at the larval and pupal stages. For these and all subsequent images of the larval eye disc, anterior is to the left, mutant tissues are marked by the absence of GFP. (A–F) Pupal eye discs containing indicated mutant clones were stained with Phalloidin to visualize bristles (A–C) or anti Cut antibody to visualize developing cone cells (D–F). Arrows in (D–F) point to ommatidia with different numbers of cone cells. (G–L’) 3rd instar larval eye discs containing indicated mutant clones were stained with anti Elav antibody to visualize developing photoreceptors (G–I’) and anti Sens antibody to visualize developing R8 cells (J–L’). Arrows in (I’) show delayed photoreceptor differentiation in rbf,rno clones relative to neighboring wild-type tissue. Arrows in K–L’ point to occasional “multiple-R8” phenotype in rno clones (arrows in K and K’) and more frequent multiple-R8 phenotype in rbf,rno (arrows in L and L’). (M–Q) Sens and Elav co-labeling in rbf,rno clones showed that multiple-R8s were present within single Elav clusters (yellow arrows in M–Q).