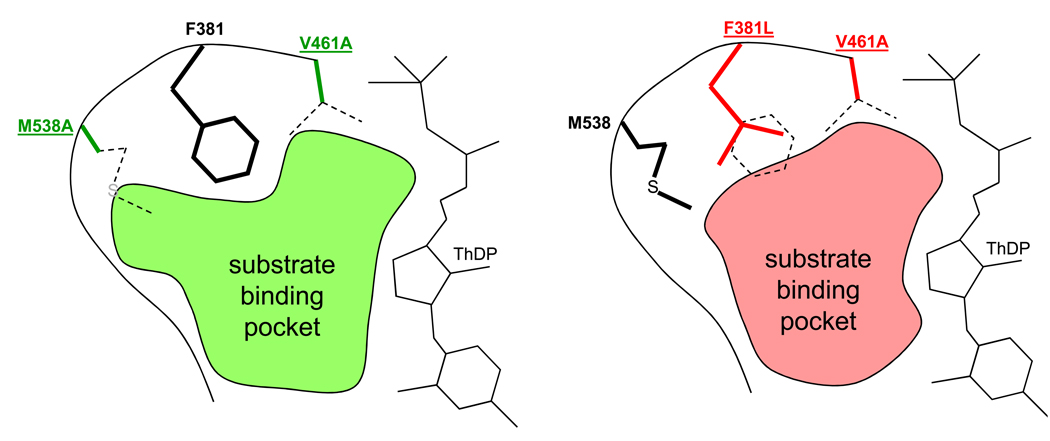
Figure 2.
A schematic stereoview of the active site of ketoisovalerate dehydrogenase (KIVD) [30]. In order to produce long-chain alcohols (C5–C8) from amino acid biosynthetic precursors, the active site of KIVD was modeled and altered to fit larger substrates. The shaded areas are representations of altered binding pockets and those of double mutants M538A/V461A (green) and F381L/V461A (red), which offer less steric hindrance to larger substrates like 2-keto-4-methylhexanoate. Dotted side chains are wild-type and highlight the changes in the substrate binding pocket as a result of mutations. ThDP: thiamine diphosphate, a co-substrate.