Fig. 4.
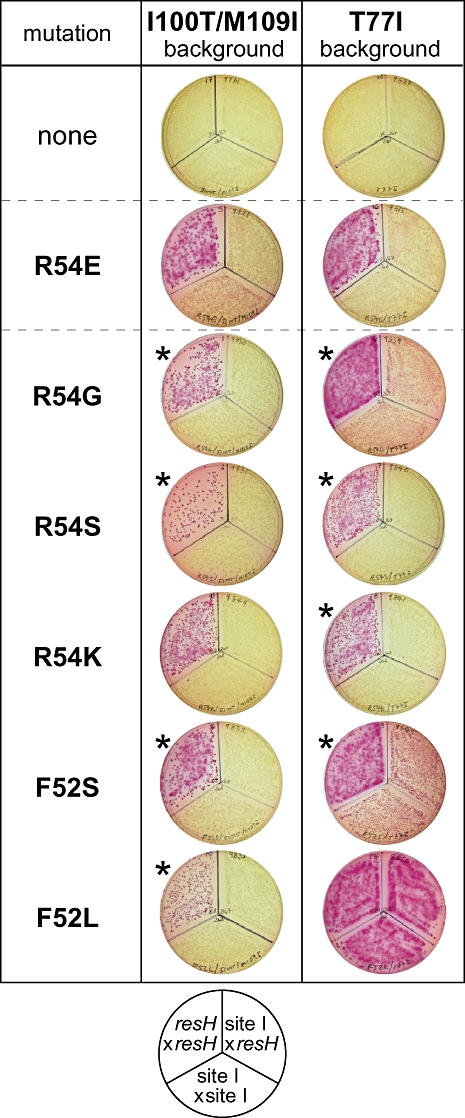
Selection of a class of Sin mutations that inhibit resH × resH recombination. Libraries of random mutants, constructed in the activated mutant backgrounds I100T/M109I and T77I (see text), were screened for mutants that can recombine a site I × site I substrate, but are defective in recombination of a resH × resH substrate. The assays show how the selected mutations, and R54E, affect recombination of resH × resH, resH × site I and site I × site I substrates in the I100T/M109I and T77I backgrounds; an asterisk indicates that the mutation was isolated in that background. White colonies indicate efficient recombination; red colonies indicate slow, or no, recombination.
