Fig. 1.
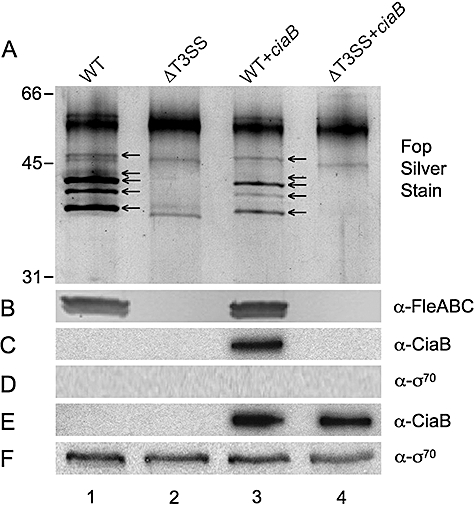
The C. jejuni CiaB protein is secreted via the Y. enterocolitica flagellar T3SS. Supernatants (A–D) and whole-cell lysates (E and F) were analysed by SDS-PAGE coupled with silver staining or immunoblot analysis. A. Silver stain showing the flagellar outer proteins (Fops) and FleABC. B. Immunoblot probed with the flagellin antibody (FleABC, 38–40 kDa). C. Immunoblot probed with the CiaB antibody (CiaB, 73 kDa). D. Immunoblot probed with the RNA polymerase σ70 antibody. E. Immunoblot probed with the CiaB antibody. F. Immunoblot probed with the σ70 antibody. Lanes: 1, Y. enterocolitica wild-type harbouring the empty pMMB207 vector (WT); 2, Y. enterocolitica pYV8081–ΔflhDC ysaT flagellar mutant harbouring the empty pMMB207 vector (ΔT3SS); 3, Y. enterocolitica wild-type harbouring the pMMB207 vector containing the C. jejuni ciaB gene (WT + ciaB); and 4, Y. enterocolitica pYV8081–ΔflhDC ysaT flagellar mutant harbouring the pMMB207 vector containing the C. jejuni ciaB gene (ΔT3SS + ciaB).
