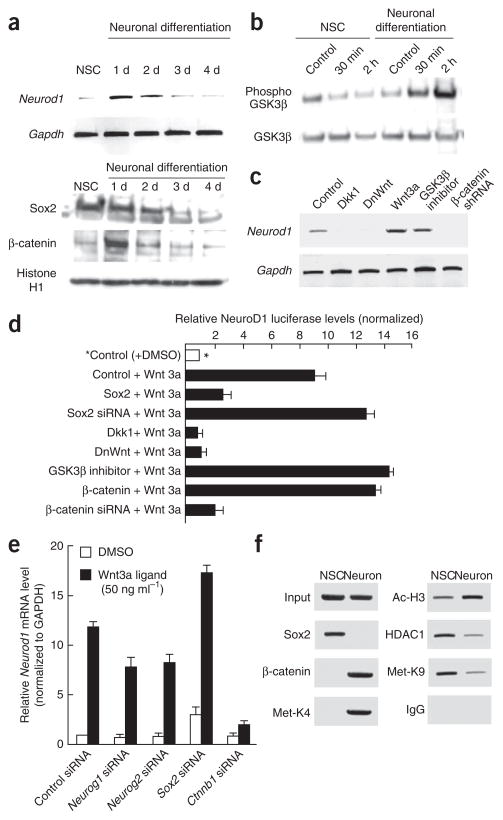
Figure 3.
Wnt signaling increases Neurod1 promoter activity during early neurogenesis. (a) Time course of Neurod1 mRNA expression during the early stages of neurogenesis in cultured adult NSCs. RT-PCR detection of Neurod1 and Gapdh is shown. Western blots of Sox2 and β-catenin during neurogenesis in cultured adult NSCs are shown in the lower panels. (b) Induction of a phosphorylated inactive form of GSK3β to stabilize β-catenin during Wnt signaling in early committed neurogenic cells. Western blots of both GSK3β and phosphorylated GSK3β were conducted using the same neuronal induction treatment. (c) The effect of Wnt signaling on the expression of Neurod1 mRNA. RT-PCR analysis using total RNA extracted from adult NSCs treated with Dkk1, DnWnt, Wnt3, TDZD8 or β-catenin shRNA. (d) The effect of Wnt signaling on the promoter activity of the Neurod1 gene. The luciferase value was normalized to that of cultured NSC sample with control vector and control ligand (DMSO, asterisk, white bar). (e) The effect of siRNAs targeting Neurog1, Neurog2, Sox2 and β-catenin on Wnt3a ligand–mediated induction on Neurod1 mRNA. qRT-PCR analysis for Neurod1 mRNA was plotted. The amount of mRNA present for each sample was normalized to that of Gapdh and then plotted as the fold increase over the control (control siRNA with DMSO). (f) ChIP analysis at the Neurod1 promoter in adult neurogenesis. PCR primers were designed to surround the Sox/LEF sequence on the rat Neurod1 promoter.