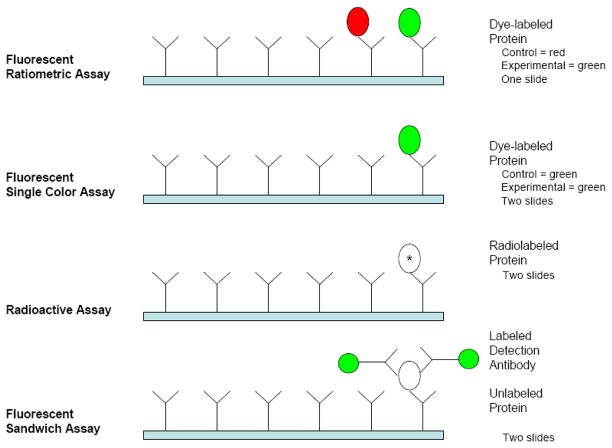
Figure 3. Antibody microarray assay methods.
Four methods of performing an antibody microarray experiment showing the use of fluorescently labeled protein samples (red and green), radioactively labeled proteins (*), and unlabeled proteins (open oval). The fluorescent ratiometric assay is the easiest to implement and most cost effective. The radioactive and fluorescent sandwich assays have the greatest dynamic range (max signal: noise floor on the order of 1000:1). Dye labeled protein assays are easier to implement with large arrays (200–700 antibodies spotted in duplicate) due to complications of detection spatial sensitivity (radioactive assays) and cross-reactions among detection antibodies (sandwich assay). Potential interactions among detection antibodies limit the number of antibodies per array to 20–40 for the sandwich assay.