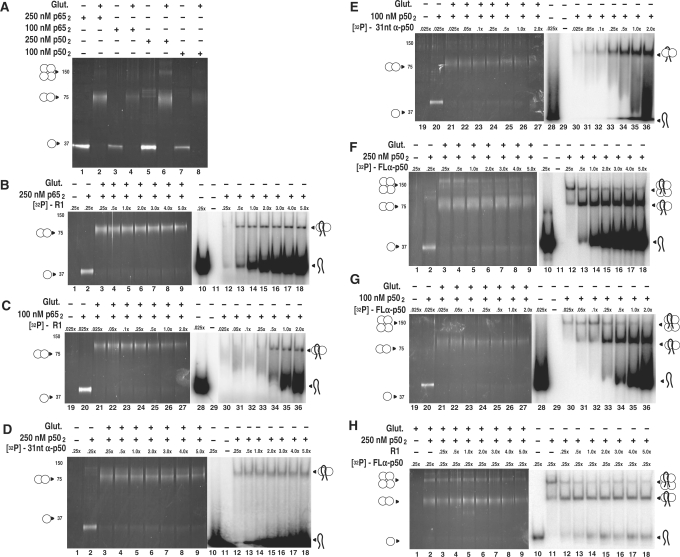
Figure 2.
RNA aptamer specificities for different NF-κB multimers. (A) Glutaraldehyde cross-linking of p50 and p65 proteins at 100 nM and 250 nM nominal dimer concentrations. (B) and (C): R1 RNA titration of p652/R1 RNA complexes. Increasing concentrations of labeled R1 RNA (0.25-, 0.5-, 1-, 2-, 3-, 4-, 5-fold relative to 250 nM p652) were incubated with p652 and electrophoresed on native gels (lanes 1–7) or cross-linked with 0.03% glutaraldehyde (Glut.) and electrophoresed on denaturing SDS gels (lanes 8–14). The analysis was repeated for 100 nM p652. (D) and (E): 31-nt anti-p50 RNA titration of p502/31-nt anti-p50 RNA complexes, performed as in (A). (F) and (G): Full-length anti-p50 RNA titration of p502/full-length anti-p50 RNA complexes, performed as in (A). (H) Competition assay of full-length anti-p50/p504 complex. Labeled full-length anti-p50 RNA was incubated at a concentration of 0.25-fold relative to 250 nM p652, with or without 0.03% glutaraldehyde (lanes 1 and 9, respectively) or in the presence of unlabeled R1 RNA competitor (non-specific for p50; 0.25-, 0.5-, 1-, 2-, 3-, 4-, 5-fold) relative to 250 nM p652, and electrophoresed on a native gel (lanes 2–8), or incubated with 0.03% glutaraldehyde and electrophoresed on a denaturing SDS gel. (lanes 10–16).