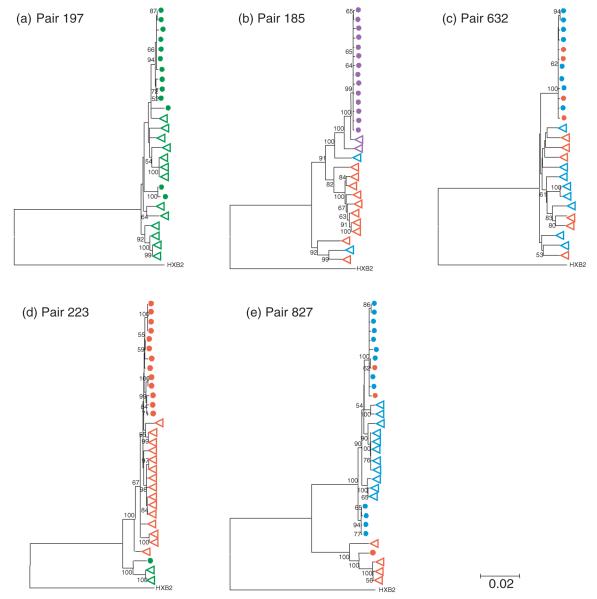
Fig. 1. Phylogenetic relationships among env clones from each mother–infant pair.
Phylogenetic trees were constructed from gp160 nucleotide sequences using neighbor-joining methods. Nodes with less than 50% bootstrap support were collapsed. Maternal and infant sequences are indicated with open triangles and filled circles, respectively. Coreceptor tropism of individual env clones is depicted in color: red, R5-tropic; blue, dual-R-tropic; purple, dual-X-tropic; green, X4-tropic. (a) Pair 197; (b) pair 185; (c) pair 632; (d) pair 223; (e) pair 827.  , Infant’s R5-tropic clones;
, Infant’s R5-tropic clones;  , Infant’s X4-tropic clones;
, Infant’s X4-tropic clones;  , Infant’s dual-R clones;
, Infant’s dual-R clones;  , Infant’s dual-X clones;
, Infant’s dual-X clones;  , Mother’s R5-tropic clones;
, Mother’s R5-tropic clones;  , Mother’s X4-tropic clones;
, Mother’s X4-tropic clones;  , Mother’s dual-R clones;
, Mother’s dual-R clones;  , Mother’s dual-X clones.
, Mother’s dual-X clones.