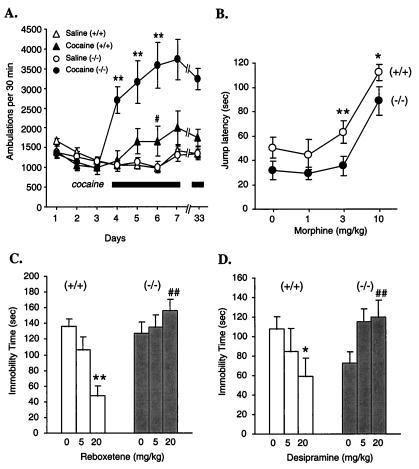
Figure 5.
Altered behavioral responses. (A) Locomotor activity. Twelve mice of each genotype were injected with saline (i.p.) on days 1–3. On days 4–7, half of the mice in each group received cocaine injections (D, 20 mg/kg, i.p.), followed by a repeat injection on day 33 (10 mg/kg). The other half received saline. ANOVA results: **, P < 0.01 Gzα(−/−) vs. wild-type; #, P < 0.05 for wild-type day 6 vs. day 4. (B) Morphine analgesia. Gzα(+/+) and (−/−) mice were divided into four groups: saline (n = 20), morphine (1.0 mg/kg, n = 14), morphine (3.0 mg/kg, n = 20), and morphine (10 mg/kg, n = 12). Student's t test for Gzα(+/+) vs. Gzα(−/−): *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01. (C and D) Antidepressant effects of desipramine and reboxetine in the forced swimming test. The data are presented as mean ± SEM. For the desipramine study: Gzα(+/+), saline n = 15, 5.0 mg/kg, n = 10, 20.0 mg/kg, n = 15; Gzα(−/−), saline n = 14, 5.0 mg/kg, n = 10, 20 mg/kg, n = 14. For the reboxetine study, n = 10 for all groups. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01 vs. respective saline control; ##, P < 0.01 vs. wild-type group under the same treatment condition. ANOVA yielded significant gene × drug interaction terms for desipramine [F(2, 72) = 6.16, P < 0.005] and reboxetine [F(2, 54) = 8.51, P < 0.01].