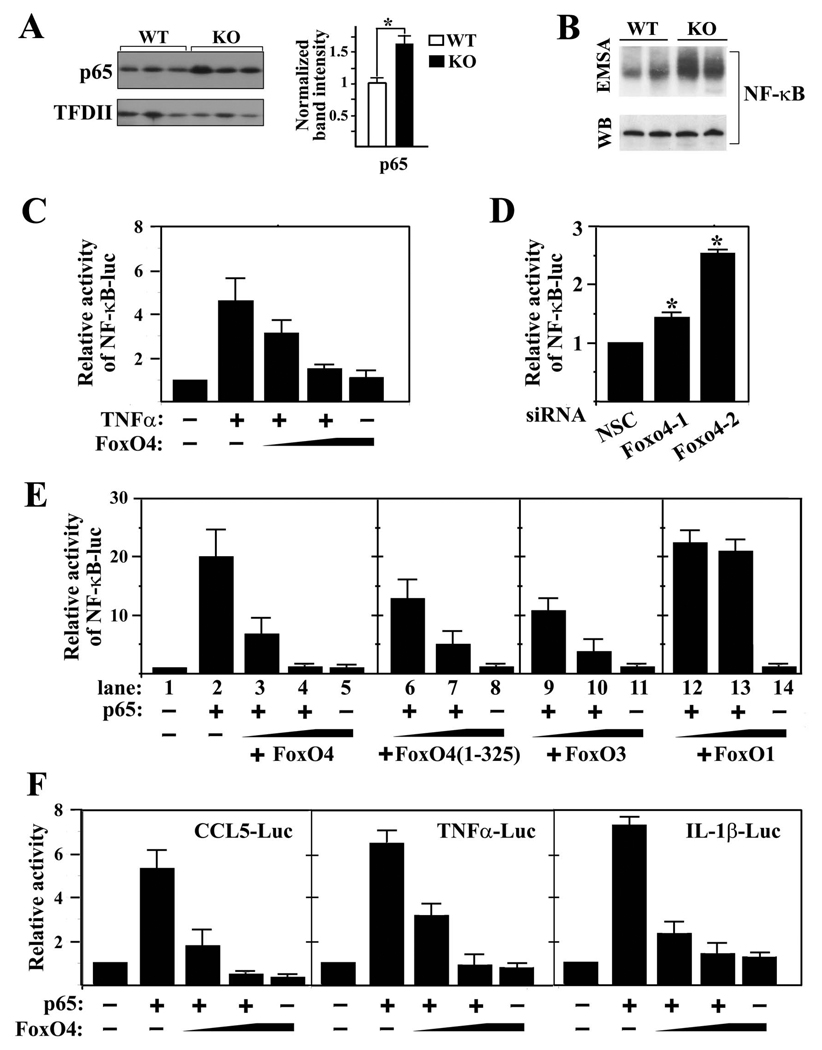
Figure 5. FoxO4 inhibits the transcriptional activity of NF-κB.
(A) Western blot of nuclear NF-κB from colonic epithelial cells of WT and Foxo4-null mice. TFDII was used as loading control (n=3±SEM, *,p<0.05). (B) NF-κB DNA binding activities from colonic mucosa of WT and Foxo4-KO mice were measured using electrophoretic mobility shift assay (EMSA) with a κB oligonucleotide probe. Representative results from two WT and two Foxo4-KO mice are shown. Total p65 protein level was used as a loading control. (C) NF-κB-luc reporter activity from caco-2 cells transfected with a NF-κB-luc reporter and increasing amount of FoxO4 plasmid. The reporter was activated by endogenous NF-κB upon stimulation with TNFa (20 ng/ml) (n=3 ± SEM). (D) The basal activity of NF-κB in Foxo4 knocked down caco-2 cells was measured using NF-κB-luc reporter (n=3 ± SEM, *, p<0.05). (E) NF-κB-luc reporter activity from 293T cells transfected with a NF-κB-luc reporter and various constructs as indicated (n=3 ± SEM). (F) Luciferase reporter activities from 293T cells transfected with the indicated plasmids (n=3 ± SEM).