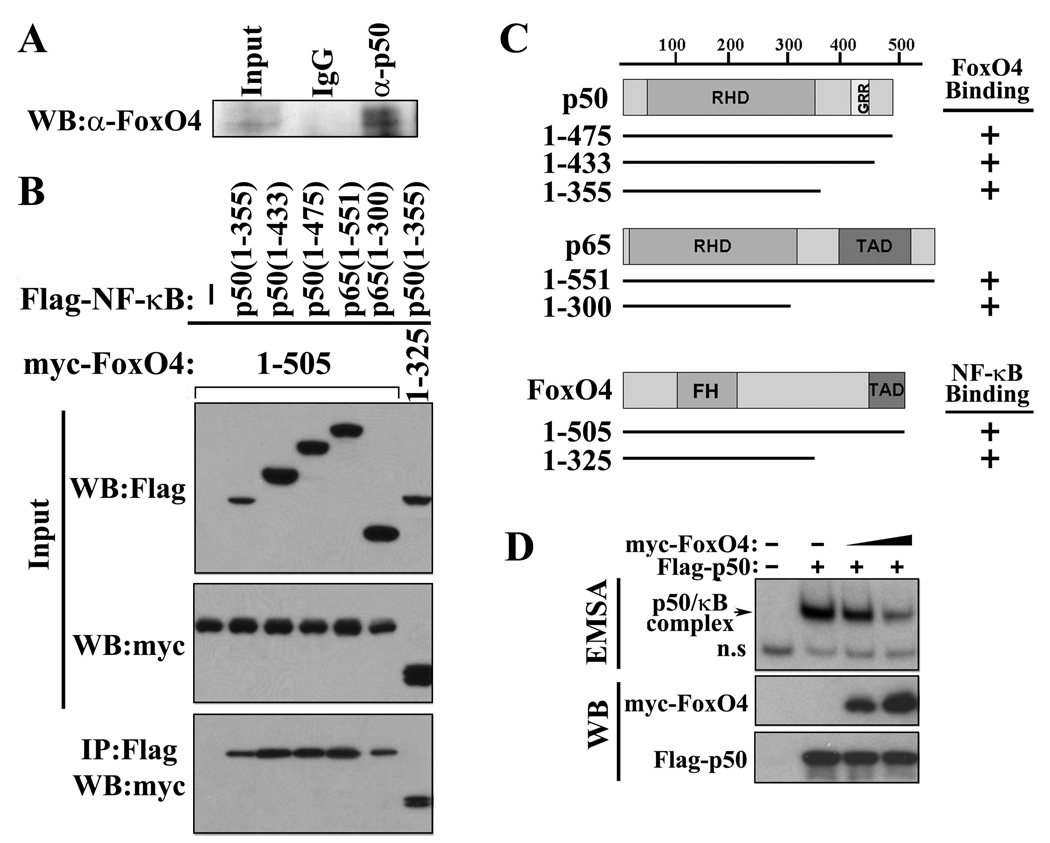
Figure 6. FoxO4 interacts with NF-κB and inhibits its DNA binding activity.
(A)Endogenous NF-κB p50 and FoxO4 from mouse colonic epithelial cells were co-immunoprecipitated (IP) with control IgG and anti-p50 antibody. Immunoprecipitates were subjected to western blot (WB) analysis and probed with anti-FoxO4 antibody. (B) 293T cells were transfected with indicated expression plasmids. Cell lysates were used for IP with anti-Flag antibody, and the immunoprecipitates were analyzed by WB with anti-myc antibody. Five percent of inputs are shown. TAD, transactivation domain. GRR, glycine rich region. (C) Schematic diagram of plasmids used in (B). (D) Protein extracts from 293T cells transfected without and with NF-κB Flag-50 and increasing amount of myc-FoxO4 were used for an EMSA (upper panel) and for western blot analysis with anti-Flag and anti-myc antibody (lower panels).