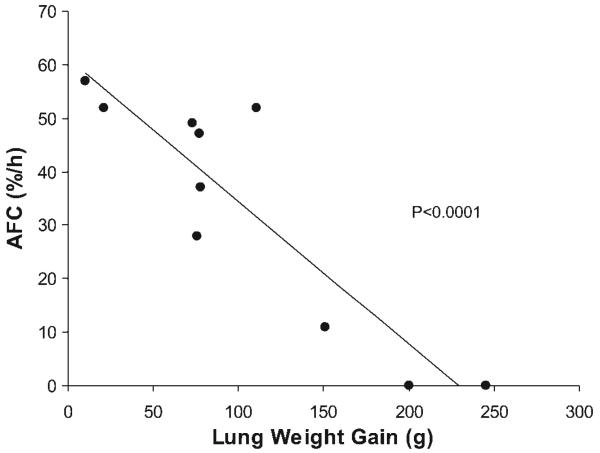
Fig. 6.
AFC is inversely associated with pulmonary edema in the perfused lung model. For the 10 lungs in which albumin flux and AFC were measured, higher stimulated AFC rates were associated with less weight gain (pulmonary edema) (Pearson coefficient −0.90, r 2 = 0.8, P < 0.0001). Basal AFC was also associated with less lung weight gain (Pearson coefficient −0.70, r 2 = 0.5, P < 0.02) (not shown).