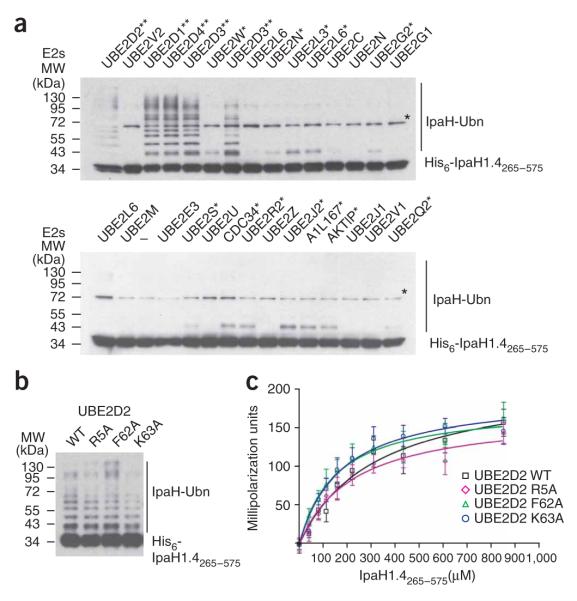
Figure 7.
IpaH interactions with E2 conjugating enzymes. (a) Immunoblot analysis using anti-IpaH antibodies of reactions performed in the presence of ATP, ubiquitin, E1, IpaH1.4265–575 and one of the indicated human E2 enzymes. The reactions were performed at 25 °C for 40 min. The double asterisk indicates the E2s supporting the strong autoubiquitination reaction. Single asterisk indicates the E2s supporting formation of only a single modified species. A star indicates the (70 kDa) species that is present in all lanes, including the one that did not contain any E2 (below, third lane). This band would correspond to a dimer of IpaH1.4265–575, presumably formed through a disulfide bond between cysteine residues in IpaH265–575 monomers (see also Fig. 1). The E2 nomenclature is in accordance with that used by the Human Genome Organization (http://www.genenames.org/genefamily/ube2.php). The reaction with UBE2D3 E2 was done in duplicate (above, lanes 5 and 7). (b) Immunoblot analysis using anti-IpaH antibodies showing IpaH1.4265–575 autoubiquitination in the presence of wild type (WT) and R5A, F62A and K63A UBE2D2 variants. Reactions were performed at 25 °C for 5 min. (c) Determination of the dissociation constants of IpaH1.4265–575 interactions with UBE2D2 using fluorescence polarization. The change in fluorescence polarization of fluorescein-labeled UBE2D2 (WT) or its indicated variants are plotted as a function of IpaH1.4265–575 concentration with error bars indicating s.d.