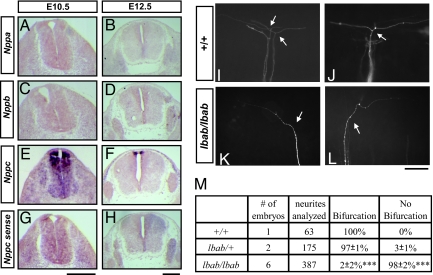
Fig. 1.
CNP is expressed in the dorsal spinal cord and required for sensory axon bifurcation. (A–H) Expression of NPs in the spinal cord and DRG revealed by digoxigenin-labeled RNA probes for NP precursors Nppa (A and B), Nppb (C and D), and Nppc (E and F) in the cross sections of E10.5 (A, C, E, and G) and E12.5 (B, D, F, and H) mouse embryos. A sense probe for Nppc was used as a control (G and H). (Scale bar: 500 μm.) (I–L) Disruption of DRG afferent bifurcation in the lbab mutant embryos is revealed by DiI labeling at the single-cell resolution. Images were taken from the lateral side of E13.5 spinal cords. Normally in the wild-type (+/+) spinal cord, sensory axons bifurcate (arrows) at the DREZ, resulting in 2 daughter branches that extend in opposite directions (I and J). However, in the lbab mutant spinal cords (K and L), 1 of the branches is missing, whereas the other appears to grow normally by extending in either the rostral or the caudal direction after turning (arrows). (Scale bar: 100 μm.) (M) Quantification of the DiI analysis in I–L. The percentage of bifurcated axons is listed for comparison between different genotypes (mean ± SD from 3 litters). Almost none of the afferents bifurcate in the lbab mutants as compared to the wild-type or heterozygote littermates (***, P < 0.001, t test). The number of embryos and the number of afferents analyzed are also included.