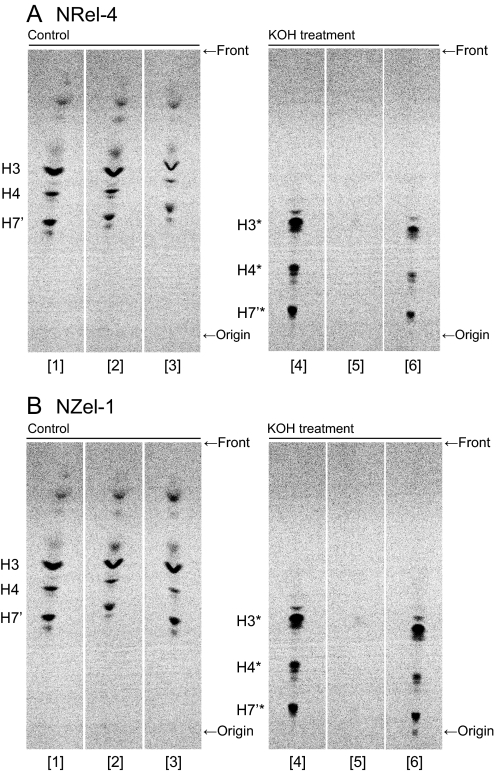
Fig. 3.
Roles of DHAP-ATase (A) and alkyl-DHAP synthase (B) in GPI biosynthesis. (A) Parental CHO-K1 cells (lanes 1 and 4), DHAP-ATase defective NRel-4 cells (lanes 2 and 5), and DHAP-ATase-transfected NRel-4 cells (lanes 3 and 6) were metabolically labeled with D-[2–3H]mannose in the presence of BE49385A, PIG-N-inhibitor, to accumulate late GPI precursors. The extracted lipids were treated with methanol as a control (lanes 1 to 3) or 0.1 N KOH in methanol (lanes 4 to 6) for 1 h and analyzed by TLC with a solvent system of chloroform/methanol/H2O (10:10:3). H3-H7′, mannose-containing GPI precursors; H3*-H7′*, alkali-resistant part of H3-H7′. (B) Parental CHO-K1 cells (lanes 1 and 4), alkyl-DHAP synthase defective NZel-1 cells (lanes 2 and 5), and alkyl-DHAP synthase-transfected NZel-1 cells (lanes 3 and 6) were analyzed in a similar way as panel (A). These are representative data of the similar experiments repeated three times.