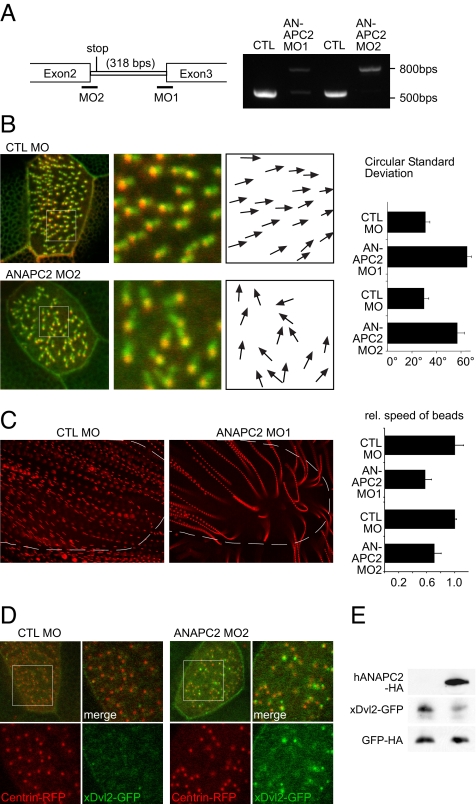
Fig. 5.
Depletion of ANAPC2 causes ciliary polarity defects. (A) The efficiency of two nonoverlapping, splice-blocking ANAPC2 MOs was monitored by RT-PCR. (B) The two MOs were injected into the ventral blastomeres to preferentially target the APC/C activity in the Xenopus epidermis. Depletion of Xenopus ANAPC2 caused a randomization of the position of the rootlet, labeled by CLAMP-GFP, in relationship to the basal body, marked by Centrin-RFP. The polarization was quantified by angular measurements of all CLAMP/Centrin pairs in 10 cells; white boxes show the magnified areas, and arrows indicate the direction of the ciliary rootlet in relation to its basal body. Depletion of ANAPC2 by either ANAPC2 MO increased the circular standard deviation compared with that of controls (P < 0.001; error bars represent SEM, n = 10). (C) The randomized polarization of the motile cilia resulted in a significantly reduced speed of fluorescent particles applied to the Xenopus epidermis. Single particles, tracked by Imaris 6.0 software, were depicted as streamlines after superimposing the single frames of video recordings. Broken lines depicted the positions of the embryos. Because of the decreased speed, the streamlines of ANAPC2-MO-injected tadpoles are more punctuated, and the distances between individual dots are smaller (P < 0.05; error bars represent SEM, n > 10). In addition, some particles showed disordered movements and circular trajectories toward the end of the tracked movements. (D) Low levels of xDvl2-GFP (50 pg) were coexpressed with Centrin-RFP (200 pg) in epidermal ciliated cells. Larger magnifications of the boxed area are at right. Channels are separated. In embryos injected with the control (CTL) MO, the xDvl2-GFP signal was barely detectable, whereas xDvl2-GFP formed visible aggregates in Xenopus embryos coinjected with ANAPC2 MO. (E) In whole-embryo lysates, overexpression of human ANAPC2 reduced the steady-state levels of xDvl2-GFP. The RNA coding for xDvl2-GFP and HA-tagged GFP were coinjected without (Left) or with ANAPC2 mRNA (Right) into four-cell-stage embryos. Embryo lysates were prepared at stage 10.5 and analyzed for protein levels by Western blot. Although ANAPC2 reduced xDvl2-GFP levels, the levels of GFP remained unaffected by ANAPC2.