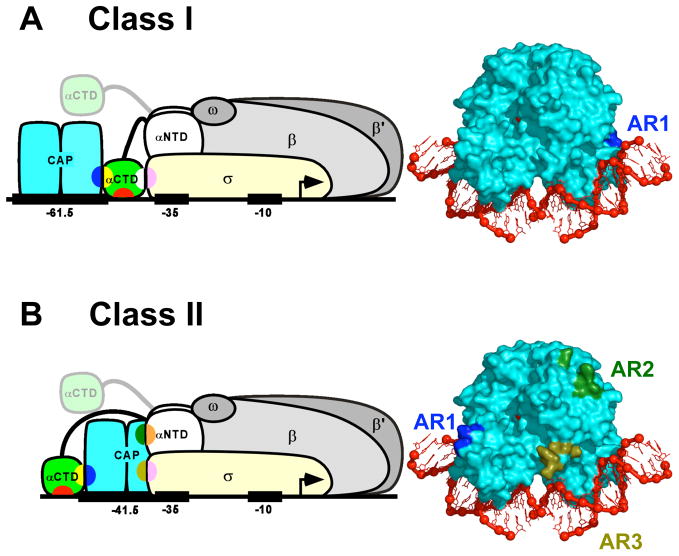
Figure 3.
Transcription activation by CAP: schematic models and activating regions.
(A) Transcription activation at a Class I CAP-dependent promoter [1,40**]. Left: Ternary complex of CAP, RNAP, and a Class I CAP-dependent promoter having the DNA site for CAP centered at position -61.5 [e.g., lac or CC(-61.5)]. Transcription activation involves interaction between AR1 of the downstream subunit of CAP (blue) and the “287 determinant” of one αCTD protomer (yellow). The AR1-αCTD interaction facilitates binding of αCTD, through its “265 determinant” (red), to the DNA segment immediately downstream of CAP and, through its “261 determinant” (white), to residues 573–604 within σR4 (pink). The second αCTD protomer (positioned arbitrarily in figure) interacts non-specifically with upstream DNA [1,39,41]. Right: Structure of the CAP-DNA complex showing AR1 of the downstream subunit (blue).
(B) Transcription activation at a Class II CAP-dependent promoter [1,58,59]. Left: Ternary complex of CAP, RNAP, and a Class II CAP-dependent promoter having the DNA site for CAP centered at position −41.5 [e.g., gal or CC(−41.5)]. Transcription activation involves three sets of CAP-RNAP interactions: (i) interaction between AR1 of the upstream subunit of CAP (blue) and the “287 determinant” of one αCTD (yellow), an interaction that facilitates binding of αCTD, through its “265 determinant” (red), to the DNA segment immediately upstream of CAP; (ii) interaction between AR2 of the downstream subunit of CAP (dark green) and residues 162–165 of αNTDI (orange); and (iii) interaction between AR3 of the downstream subunit of CAP (olive green) and residues 593–603 of σR4 (pink). The second αCTD protomer (positioned arbitrarily in figure) interacts non-specifically with upstream DNA [1,62,63]. Right: Structure of the CAP-DNA complex showing AR1 of the upstream subunit (blue), AR2 of downstream subunit (dark green), and AR3 of downstream subunit (olive green).