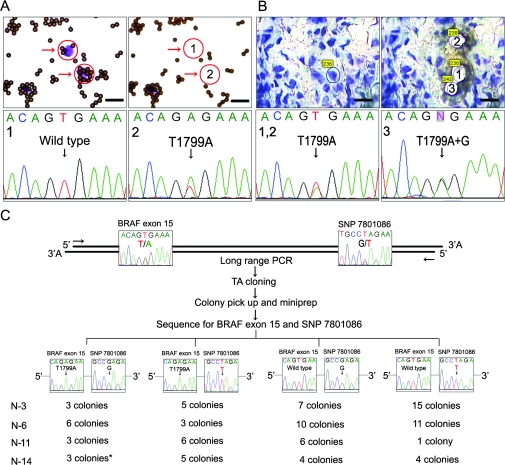
Figure 1.
Polyclonality of v-raf murine sarcoma viral oncogene homolog B1 (BRAF) mutations in acquired melanocytic nevi. A) Selection of single nevus cells after immunomagnetic separation. Single nevus cells (purple dots with arrows) were captured by high molecular weight-melanoma-associated antigen–specific monoclonal antibodies bound to immunomagnetic beads (pink dots). The cells (encircled) were procured by laser-capture microdissection (top; bar = 20 μm). Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplification and subsequent sequencing of single nevus cells showed wild-type BRAF and BRAFV600E mutations (bottom). B) Laser-capture microdissection of frozen tissue section of acquired melanocytic nevi followed by direct sequencing of BRAF exon 15 (top; bar = 20 μm). Sequencing revealed two of the contiguous single nevus cells to have the BRAFV600E mutation and one to have a compound heterozygous BRAFV600E (T1799A) and BRAFV600G (T1799G) mutation, showing a heterogeneous pattern of BRAF mutations in proximal cells on a single-cell level (bottom). C) Subcloning and subsequent sequencing of BRAF exon 15 and the single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) rs7801086. This SNP maps approximately 2 kb telomeric from BRAF exon 15. Four nevi (numbers 3, 6, 11, and 14) were excised from patients who were heterozygous for this SNP. DNA was extracted from hundreds of nevus cells isolated either by using immunomagnetic beads (numbers 3 and 6) or laser-capture microdissection of frozen tissue sections (numbers 11 and 14). A 2859-bp fragment containing both BRAF exon 15 and the SNP rs7801086 was amplified by long-range PCR. Subcloning was carried out using this fragment as an insert. Sixteen to 30 colonies were randomly picked from each patient sample and analyzed for the sequence of both BRAF exon 15 and rs7801086. In all four patient samples, colonies with BRAFV600E as well as wild-type BRAF were accompanied by different SNP alleles, some harboring the G allele and others harboring the T allele. In sample number 14, one colony (*) showed a tandem BRAFV600E/K601E (T1799→A and A1802→G) mutation.