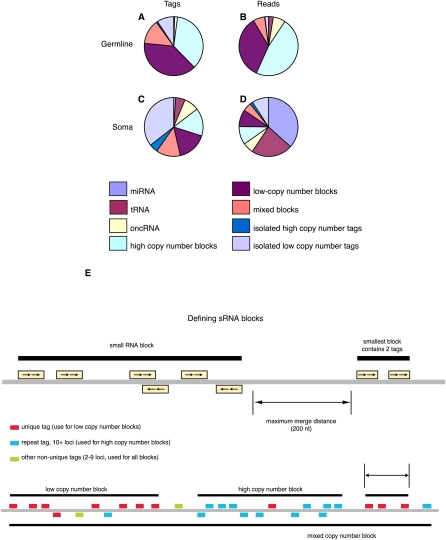
Figure 3.
(A–D) Distribution of small RNA (sRNA) types in oocytes (A,B) and somatic cells (C,D), by unique tag (A,C) and by read (B,D) count. Filtered tags were identified either by BLAST similarity to known RNA types (miRNA, tRNA, rRNA, other noncoding RNA [oncRNA]), or otherwise by occurrence in “blocks” of neighboring tags, or not. Blocks were defined by groups of tags of a given type with no gaps between neighbors greater than a fixed value (200 bases). Tag types used were single locus tags, tags with 10+ loci, and all tags, defining low copy number, high copy number, and mixed blocks, respectively. Tags not in blocks were termed isolated. (E, top) Schematic view of general method for defining short RNA blocks. (E, bottom) Different families of blocks are made using only unique mapping tags (low copy number), tags with ten or more loci (high copy number), and all tags.